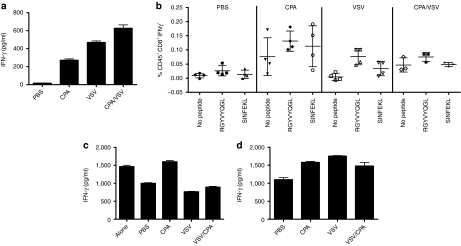
Figure 5.
VSV induces immune suppressors. (a) Splenocytes from mice treated with two rounds of PBS, CPA, VSV, or CPA/VSV were harvested 24 hours following the final injection of VSV or PBS and 106 cells were plated, in triplicate from each mouse. Forty-eight hours later, supernatants were harvested and assayed for IFN-γ by ELISA. (b) Splenocytes prepared as in a pulsed with no peptide, SIINFEKL (ova), or RGYVYQGL (VSV-N protein) were assayed for IFN-γ-producing cells by ELISPOT. (c) Naive OT-I CD8+ T cells activated with H-2Kb-restricted ova peptide SIINFEKL either alone, or with splenocytes from mice treated with PBS, CPA, VSV, or CPA/VSV 24 hours following the final injection, were assayed for IFN-γ by ELISA. The suppressive activity in splenocyte cultures is reflected by inhibition of IFN- γ responses of naive OT-I T cells activated by SIINFEKL. (d) The experiment of c was repeated in the presence of recombinant human TGF-β sRII/Fc chimera added to each OT-I/splenocyte culture in order to inhibit the activity of TGF-β which may be being secreted by the added splenocytes. CPA, cyclophosphamide; IFN-γ, interferon-γ ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; ELISPOT, enzyme-linked immunospot; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β VSV, vesicular stomatitis virus.