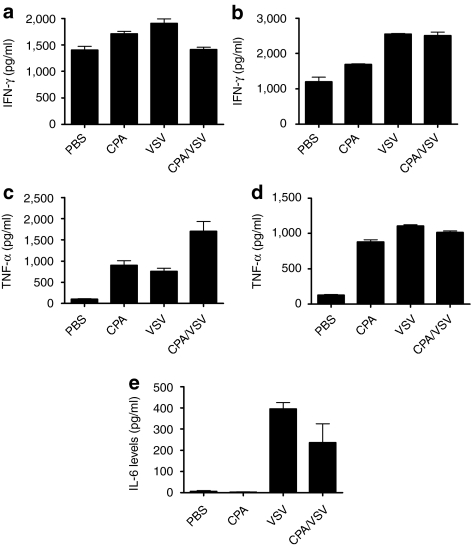
Figure 7.
VSV-induced suppression is mediated by CD11b+GR-1+ cells. (a,b) Naive OT-I CD8+ T cells were activated with SIINFEKL peptide and cocultured with splenocytes from mice treated with PBS, CPA, VSV, or CPA/VSV predepleted of either (a) GR-1+ or (b) CD11b+ cells. Seventy-two hours later, supernatants were assayed for IFN-γ. Both CPA and VSV treatments are statistically different from PBS treatment (P = 0.03 and P < 0.01, respectively in (a); all three treatments are significantly different (P < 0.01) from PBS in (c). (c,d) Supernatants from AE17ova cells cocultured with splenocytes (effector:target ratio 10:1) from mice treated with PBS, CPA, VSV, or CPA/VSV and predepleted of either (c) GR-1+ or (d) CD11b+ cells were assayed for TNF-α. In both (c) and (d) all three treatments are significantly different from PBS, P < 0.001 in all cases. (e) Tumors from mice treated as shown were assayed for IL-6. CPA, cyclophosphamide; IFN-γ, interferon-γ IL, interleukin; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α VSV, vesicular stomatitis virus.