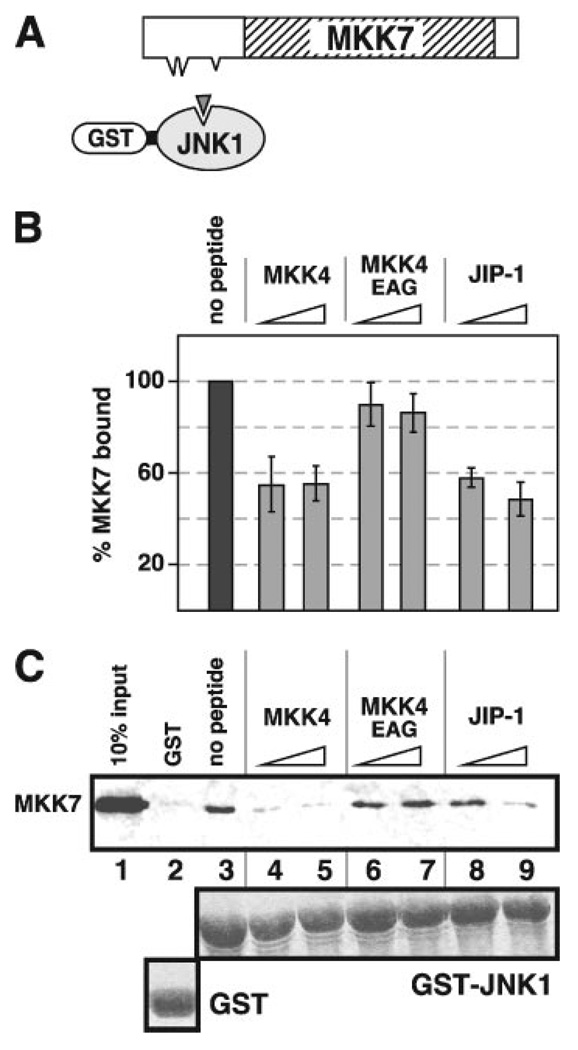
FIGURE 6. Inhibition of MKK7 binding to JNK1 by MKK4 and JIP-1 D-site peptides.
A, D-site peptides (triangle) were used to inhibit the ability of MKK7 to bind to GST-JNK1. B, quantification of peptide inhibition data. Shown is the average percent binding of MKK7 to GST-JNK1 (40 µg), normalized by setting the binding of the “no peptide” point to 100%. Standard error bars are shown (n = 4). C, 35S-labeled MKK7 was tested for binding to 40 µg of either GST or GST-JNK1. Lane 1 shows a 10% input of the MKK7 protein. Synthetic peptides (25 and 100 µm) were added to the indicated reactions to inhibit binding of MKK7 to GST-JNK1. The lower panel shows Coomassie Blue (CB) staining of the sedimented GST fusion proteins.