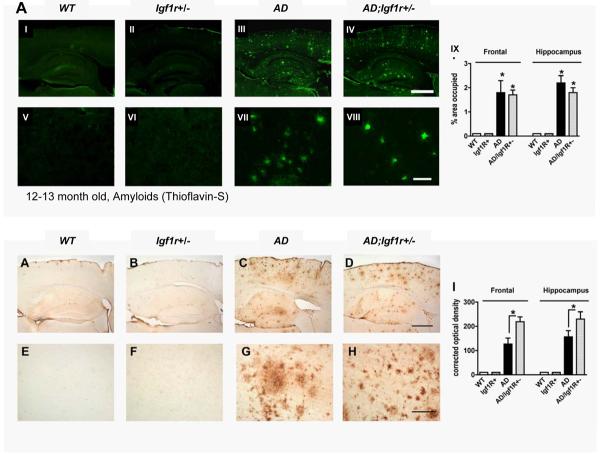
Figure 4.
Reduced IGF signaling facilitates Aβ hyper-aggregation. A. Thioflavin-S amyloid labeling showed similar Aβ plaque burden in brains of AD (panels III and VII) and AD;Igf1r+/− animals (panels IV and VIII). Image analysis indicated that the Thioflavin-S signals are similar in brains of AD and AD;Igf1r+/− mice, but signifcantly different from WT and Igf1r+/− mice (panel IX). Six 12–13 month old animals per genotype were analyzed. B. Aβ plaque signal density was measured using Aβ specific antibody (82E1). The signal per area ratio in brains of AD;Igf1r+/− animals (panels IV and VIII) was significantly higher (panel IX, P<0.05) compared to brains of age matched AD animals (panels III and VII) indicating higher plaque compaction in brains of AD;Igf1r+/− mice (six mice per genotype and 3 sections per animal were analyzed, DG – Dentate gyrus, NC – Neocortex).