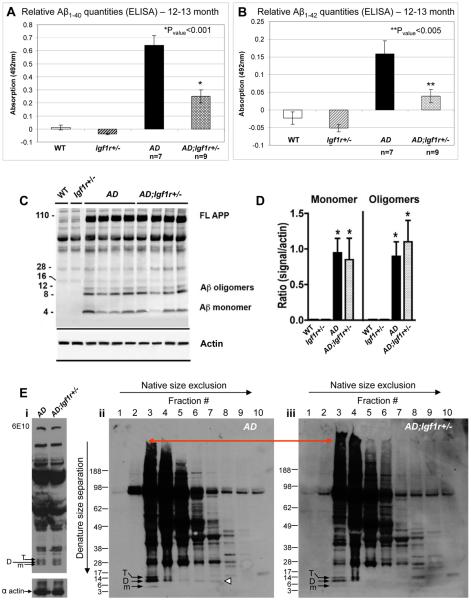
Figure 6.
AD brains contain more soluble Aβ oligomers than brains of AD;Igf1r+/− animals. A and B. ELISA assay detected significantly higher amounts of soluble Aβ1–40 (A) (P<0.001) and Aβ1–42 (B) (P<0.005) in brain homogenates of 12–13 month old AD mice compared to brains of age matched AD;Igf1r+/− animals. C and D. Western blot analysis reveals no detectable difference in the amount of SDS sensitive Aβ monomers and small oligomeric assemblies between AD and AD;Igf1r+/− brain homogenates. * indicates significant difference from WT or Igfr1+/− mice. E. Native size exclusion chromatography (SEC) indicated that Aβ dimers were mainly associated with large structures in brains of 16–17 month AD;Igf1r+/− mice (panel iii) while more soluble in brains of age matched AD animals (panel ii, arrowhead)(panels represent 6 AD and 6 AD;Igf1r+/− animals that were analyzed). Loading of total samples onto the gel and subsequent western blot analysis using 6E10, confirmed equal protein loading onto the column (panel i).