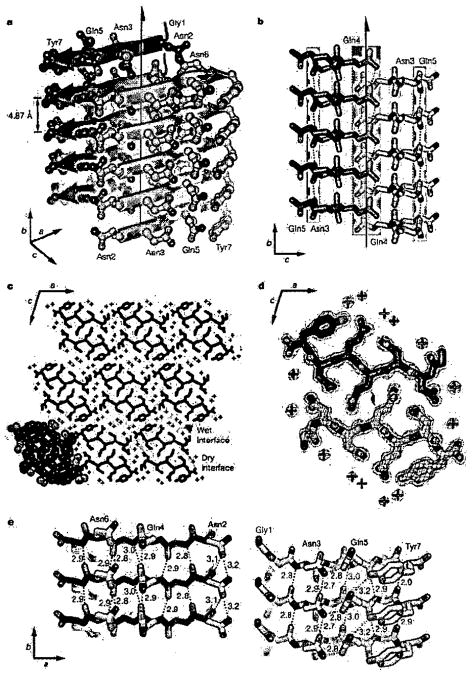
Figure 1. (from Reference 32) Structure of GNNQQNY.
a, The pair-of-sheets structure, showing the backbone of each β-strand as an arrow, with side chains protruding. The dry interface is between the two sheets, and the wet interfaces are on the outside surfaces. Side chains Asn 2, Gln 4 and Asn 6 point inwards, forming the dry interface. The 21 screw axis of the crystal is shown as the vertical line. It rotates one of the strands of the near sheet 180° about the axis and moves it up ½ × 4.87 Å so that it is superimposed on one of the strands of the far sheet. b, The steric zipper viewed edge on (down the a axis). Note the vertical shift of one sheet relative to the other, allowing interdigitation of the side chains emanating from each sheet. The amide stacks of the dry interface are shaded in gray at the center, and those of the wet interface are shaded in pale red on either side, c, The GNNQQNY crystal viewed down the sheets (from the top of panel a, along the b axis). Six rows of β-sheets run horizontally. Peptide molecules are shown in black and water molecules are red plus signs. The atoms in the lower left unit cell are shown as spheres representing van der Waals radii, d, The steric zipper. This is a close-up view of a pair of GNNQQNY molecules from the same view as panel c, showing the shape complementarity of the Asn and Gln side chains protruding into the dry interface. 2F0−Fc electron density is shown, and the position of the central screw axis is indicated, e, Views of the β-sheets from the side (down the c axis), showing three β-strands with the inter-strand hydrogen bonds. Side-chain carbon atoms are yellow. Backbone hydrogen bonds are shown by purple or gray dots and side-chain hydrogen bonds by yellow dots. Hydrogen bond lengths are noted in Å. The views of the interfaces are close to the views of panel a. The left-hand set is viewed from the center of the dry interface; the right-hand set is viewed from the wet interface. Note the amide stacks in both interfaces. Carbon atoms are purple or gray, oxygen is red, and nitrogen is blue, unless noted otherwise.