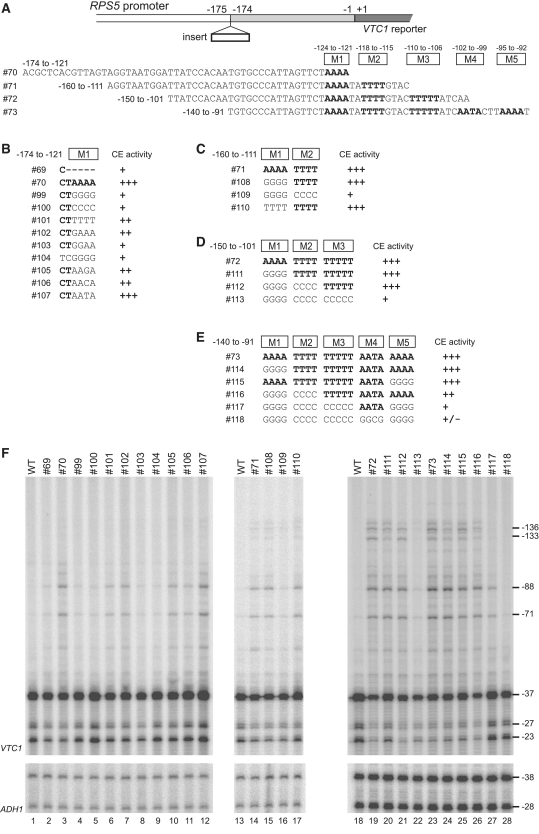
Figure 5.
Redundant CE function of multiple AT-rich sequences derived from the RPS5 promoter in ectopic initiation assays. (A) Schematic diagram showing the sequences of the RPS5 core promoter fragments tested for CE activity in (F) by inserting them at the −175/−174 bp position of the RPS5 promoter as indicated (top). The five mutated AT-rich regions (M1–M5 in B–E) are shown. (B) Sequences of #99–#107 generated from #70. CE activities in (F) are summarized at the right. (C) Sequences of #108–#110 generated from #71. CE activities in (F) are summarized at the right. (D) Sequences of #111–#113 generated from #72. CE activities in (F) are summarized at the right. (E) Sequences of #114–#118 generated from #73. CE activities in (F) are summarized at the right. (F) CE activity of each insert (#69–#73 and #99–#118 depicted in B–E) to induce ectopic initiation. Primer extension analysis was done as described in Figure 2B.