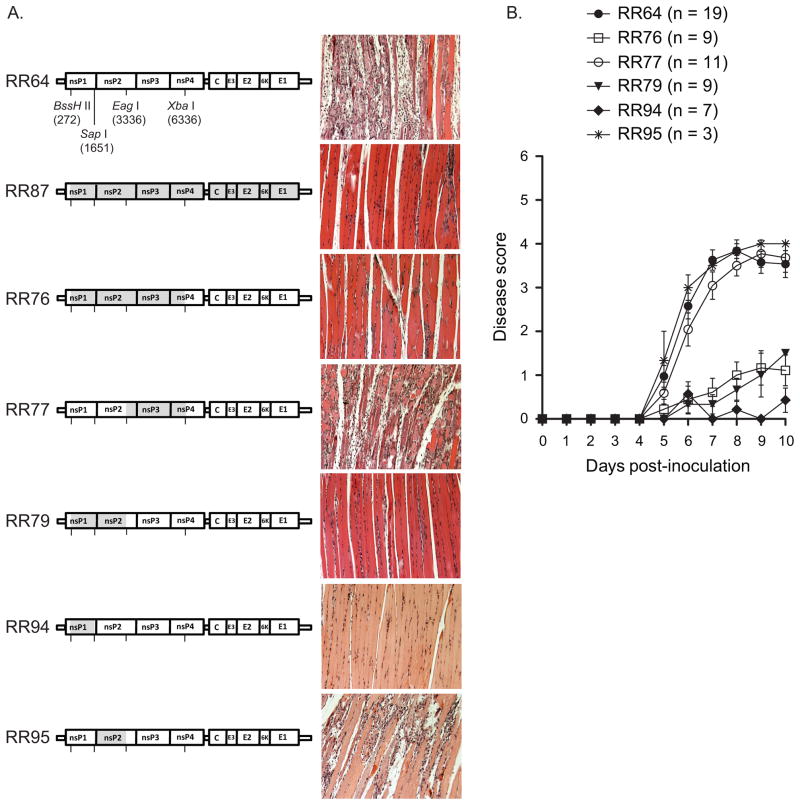
Figure 4. Chimeric viruses that encode the RRV DC5692 nsP1 coding region in the T48 strain genetic background are attenuated in vivo.
(A) Twenty-four-day-old C57BL/6J mice were inoculated with 103 PFU of RR64, RR76, RR79, RR77, RR94, or RR95 by injection in the left rear footpad. At 10 dpi, mice were sacrificed and perfused with 4% paraformaldehyde. 5 micron-thick paraffin-embedded sections generated from the quadriceps muscle were stained with H&E. Images are representative of three mice per group. (B) Twenty-four-day-old C57BL/6J mice were inoculated with 103 PFU of RR64 (n = 19), RR76 (n = 9), RR77 (n = 11), RR79 (n = 9), RR94 (n = 7), or RR95 (n = 3) by injection in the left rear footpad. Mice were scored for the development of disease signs including loss of gripping ability, hind-limb weakness, and altered gait. Each data point represents the arithmetic mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Data are combined from four independent experiments and were evaluated for statistically significant differences by ANOVA (P < 0.0001) followed by Bonferroni’s Multiple Comparison Test (see text).