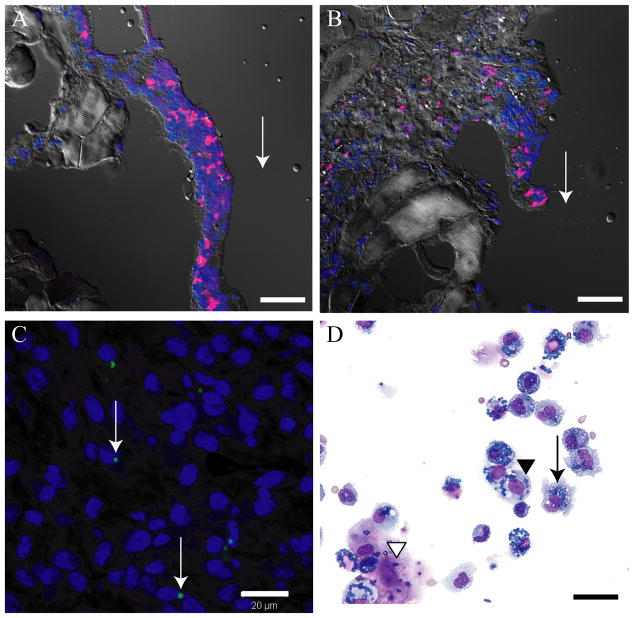
Figure 3.
Several in vivo experiments demonstrate that APMS are taken up by a variety of cell types and remain adjacent to sites of injection. (A, B) APMS-Alexa-568 (red) injected into the pleural cavity of C57BL/6 mice were found in cells lining the rib at 72 h post-injection. Cell nuclei are stained blue (TOTO-3). Arrows indicate the approximate site of APMS injections. Approximately 3.3×107 APMS-Alexa-568 were injected into individual mice (× 400, scale bars = 20 μm). (C) APMS-Alexa-488 (green) injected at the distal pole of Hmeso SC tumors grown in SCID mice were detected within the cytoplasm of individual MM cells towards the center of the tumor mass. Tumor cell nuclei are stained blue (DAPI). Arrows indicate the presence of APMS-Alexa-488 signal. Approximately 3×106 APMS-Alexa-488 were injected into individual tumors (× 400, scale bar = 20 μm). (D) Representative PLF cytospin showing co-localization of APMS with macrophages (arrow), sloughed mesothelial cells (black arrowhead), and MM cells (white arrowhead) (× 400, scale bar = 20 μm).