Figure 2.
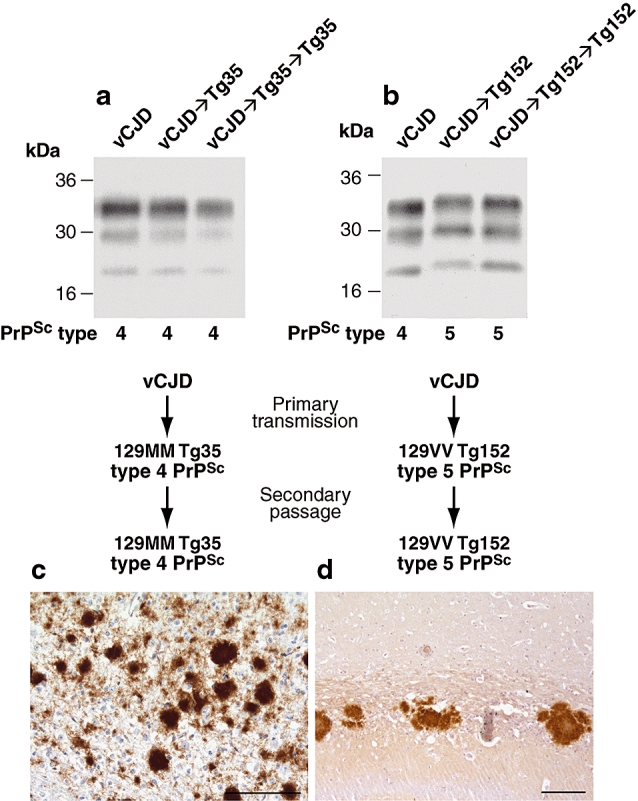
Human prion protein with valine at residue 129 prevents expression of the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) phenotype. Primary and secondary transmission of vCJD prions to transgenic Tg(HuPrP129M+/+Prnp°/°)-35 mice (Tg35) results in faithful propagation of type 4 PrPSc and the occurrence of abundant florid PrP plaques throughout the cortex that are the neuropathological hallmark of vCJD [49]. In contrast, primary transmission of vCJD prions to transgenic Tg(HuPrP129V+/+Prnp°/°)-152 mice (Tg152) produces a novel prion strain that is maintained on secondary passage in the same mice distinguished by the propagation of type 5 PrPSc and a distinct pattern of neuropathology characterized by large nonflorid PrP plaques restricted to the corpus callosum [26,49]. (a,b) Representative immuno-blots of proteinase-K treated brain homogenates from variant CJD and transgenic mice analysed with antiPrP monoclonal antibody 3F4. The identity of the brain sample is designated above each lane with the type of PrPSc present in the sample designated below using the London classification [90]. (c,d) Representative immunohistochemical analysis of transgenic mouse brain at secondary passage showing abnormal PrP plaques stained with antiPrP monoclonal antibodies ICSM 35 (a) or 3F4 (b). Scale bars: 100 µm.
