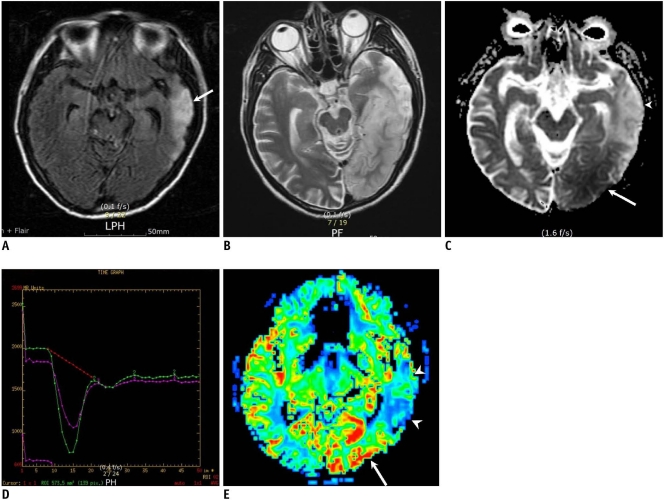
Fig. 3.
57-year-old man with two stroke-like episodes.
A. Fluid attenuated inversion recovery image obtained 18 days after first symptom onset shows infract-like lesion at left temporal lobe (arrow). B. T2-weighted image obtained on day of second attack and 17 months after prior episode shows high signal intensity in left temporooccipital lobe, including prior lesion. C. Apparent diffusion coefficient map shows diffusion restriction in posterior region of lesion (arrow), while anterior old lesion shows increased apparent diffusion coefficient (arrowhead). D. Perfusion curves (relaxivity on vertical axis and time on horizontal axis) show increased blood volume (which is proportional to signal loss) in left occipital lesion (green curve) compared to that of contralateral normal tissue (purple curve). E. Cerebral blood flow map demonstrates hyper-perfusion at newly appearing left occipital lesion (arrow), while anterior chronic lesion shows decreased perfusion (arrowheads).