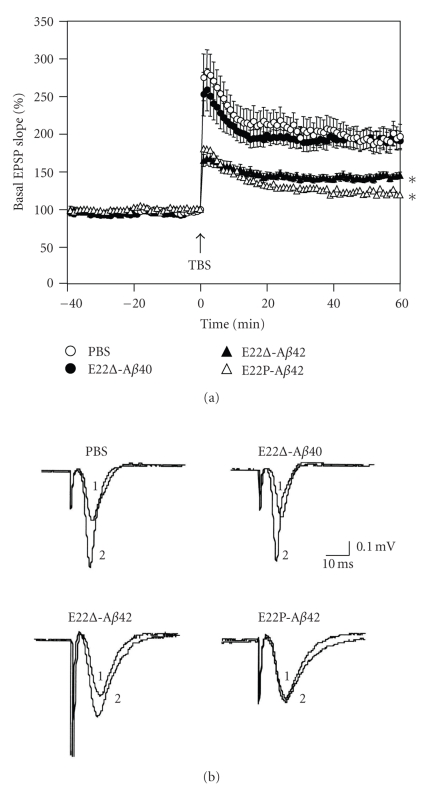
Figure 5.
In vivo synaptotoxicity of E22Δ-Aβ40, E22Δ-Aβ42, and E22P-Aβ42 estimated by LTP expression. (a) Field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) were recorded from the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices (Wistar rats, male, 6 weeks old) by delivering theta burst stimulation (TBS) to the Schaffer collateral/commissural pathway. LTP was induced by high-frequency stimulation (5 trains consisted of four 100-Hz pulses with an intertrain interval of 200 ms) in the presence and absence of each Aβ (20 μg/200 mL PBS), to be injected into the lateral ventricle 20 min before stimulation. Each point on the graph represents the mean ± s.e.m. of basal fEPSP slope (0 min); n = 12 for PBS, n = 9 for E22Δ-Aβ40, n = 10 for E22Δ-Aβ42, and n = 10 for E22P-Aβ40. *P < .0001 versus PBS; P = .4258 between PBS and E22Δ-Aβ40. P < .0001 versus PBS, when fEPSP slopes were compared with 1 to 60 min after TBS. The means between the four groups were compared using analysis of variance followed by Fisher's protected least significant difference (PLSD) test. °, PBS; ●, E22Δ-Aβ40; ▲, E22Δ-Aβ42; △, E22P-Aβ42. (b) Typical field excitatory postsynaptic potentials at (1) 0 and (2) 60 minutes after TBS.