Abstract
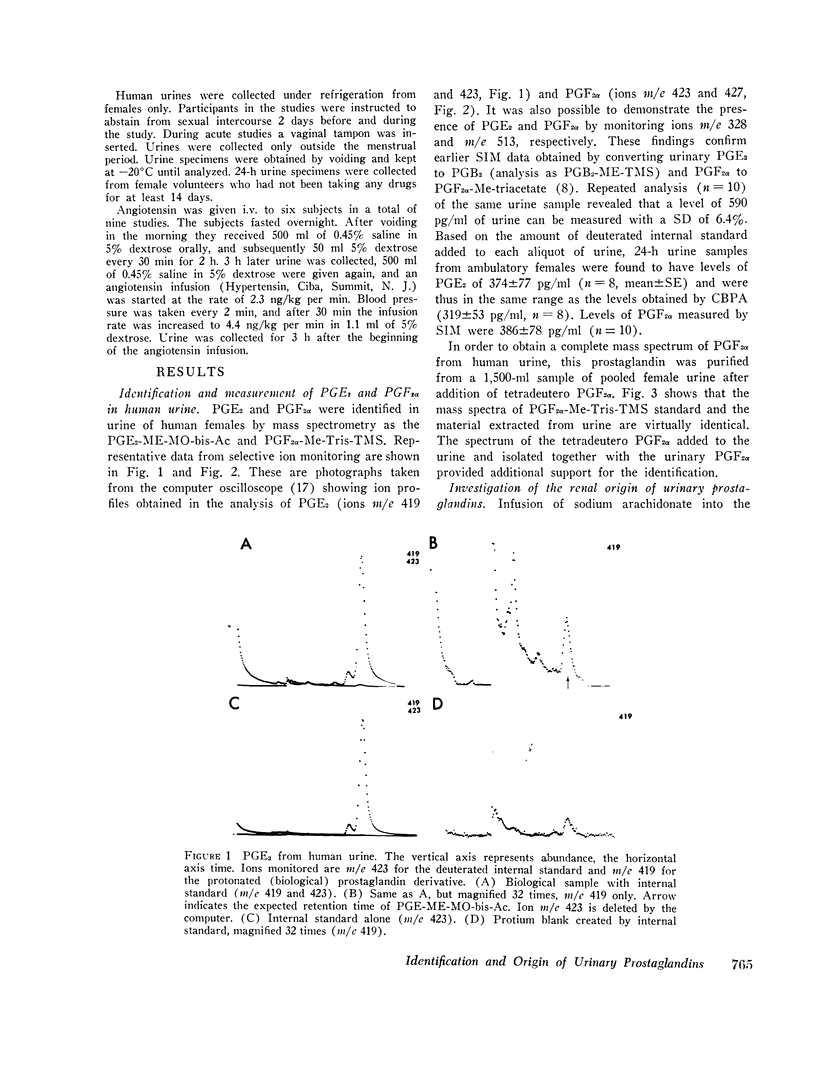
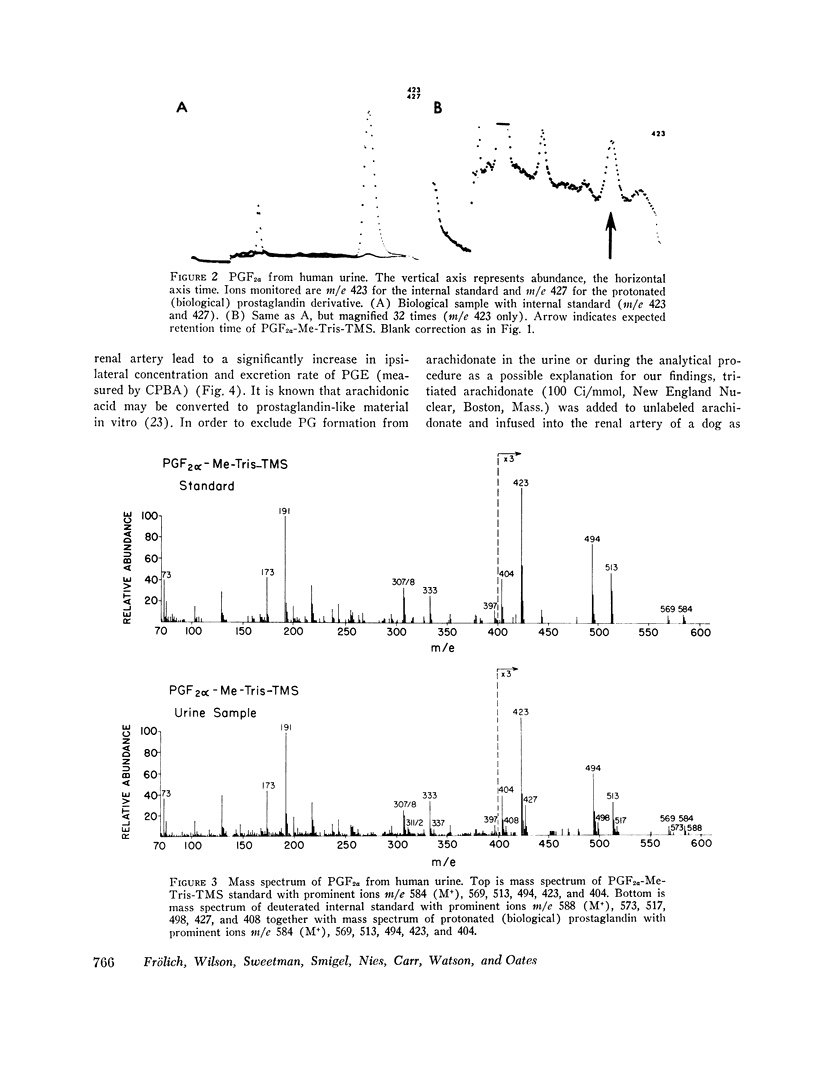
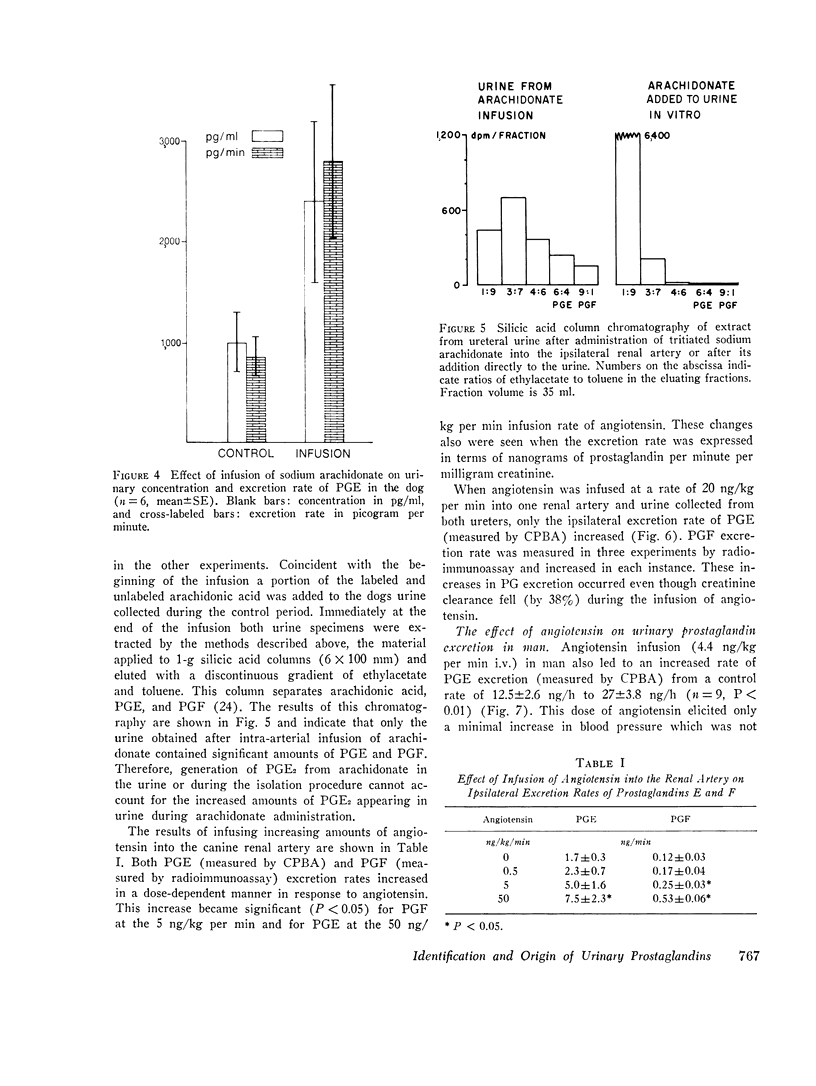
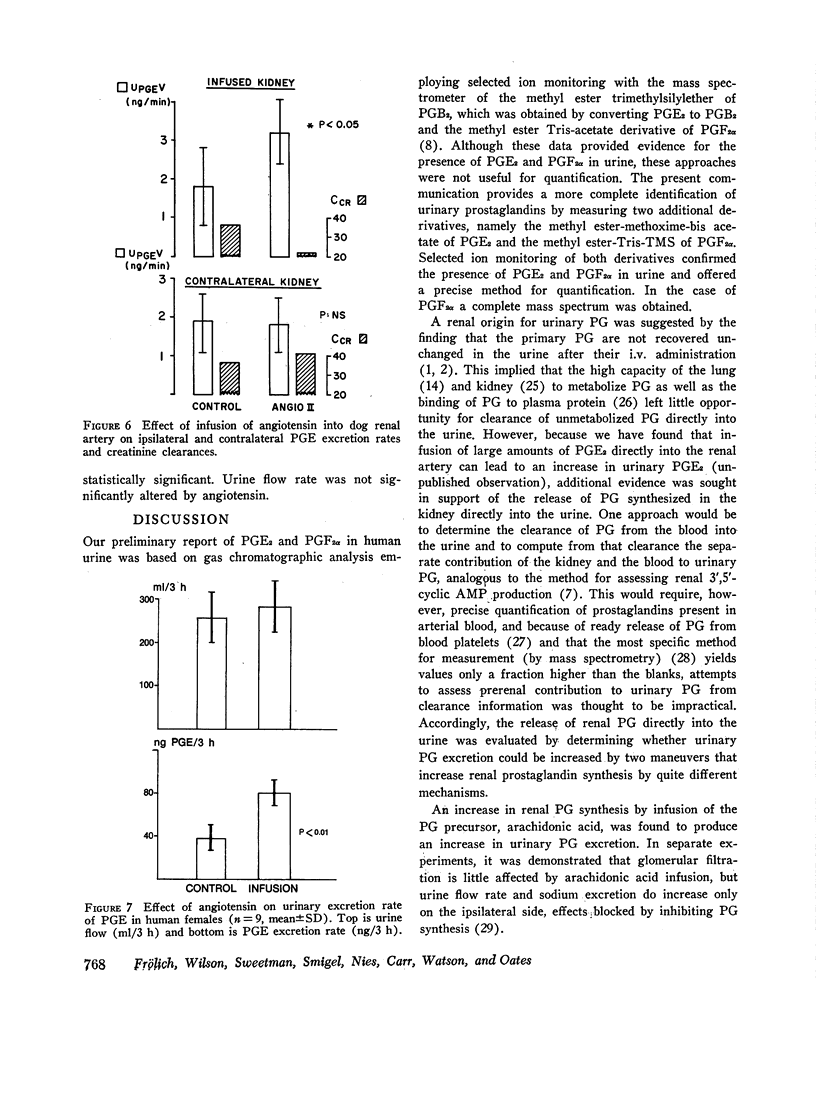
Human urine was analyzed by mass spectrometry for the presence of prostaglandins. Prostaglandin E2 and F2alpha were detected in urine from females by selected ion monitoring of the prostaglandin E2-methylester-methoxime bis-acetate and the prostaglandin F2alpha-methyl ester-Tris-trimethylsilylether derivative. Additional evidence for the presence of prostaglandin F2alpha was obtained by isolating from female urine an amount of this prostaglandin sufficient to yield a complete mass spectrum. The methods utilized permitted quantitative analysis. The origin of urinary prostaglandin was determined by stimulating renal prostaglandin synthesis by arachidonic acid or angiotensin infusion. Arachidonic acid, the precursor of prostaglandin E2, when infused into one renal artery of a dog led to a significant increase in the excretion rate of this prostaglandin. Similarly, infusion of angiotensin II amide led to a significantly increased ipsilateral excretion rate of prostaglandin E2 and F2a in spite of a simultaneous decrease in the creatinine clearance. In man, i.v. infusion of angiotensin also led to an increased urinary eliminiation of prostaglandin E. These results show that urinary prostaglandins may originate from the kidney, indicating that renally synthesized prostaglandins diffuse or are excreted into the tubule. Thus, urinary prostaglandins are a reflection of renal prostaglandin synthesis and have potential as a tool to delineate renal prostaglandin physiology and pathology.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anggård E., Bohman S. O., Griffin J. E., 3rd, Larsson C., Maunsbach A. B. Subcellular localization of the prostaglandin system in the rabbit renal papilla. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Feb;84(2):231–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anggård E., Larsson C., Samuelsson B. The distribution of 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase and prostaglandin-delta 13-reductase in tissues of the swine. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Mar;81(3):396–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axen U., Gréen K., Hörlin D., Samuelsson B. Mass spectrometric determination of picomole amounts of prostaglandins E 2 and F 2 using synthetic deuterium labeled carriers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 15;45(2):519–525. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90850-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadus A. E., Kaminsky N. I., Hardman J. G., Sutherland E. W., Liddle G. W. Kinetic parameters and renal clearances of plasma adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2222–2236. doi: 10.1172/JCI106441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bygdeman M., Samuelsson B. Analyses of prostaglandins in human semen. Prostaglandins and related factors 44. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Apr;13(4):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowshaw K., Szlyk J. Z. Distribution of prostaglandins in rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(3):421–424. doi: 10.1042/bj1160421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels E. G., Hinman J. W., Leach B. E., Muirhead E. E. Identification of prostaglandin E2 as the principal vasodepressor lipid of rabbit renal medulla. Nature. 1967 Sep 16;215(5107):1298–1299. doi: 10.1038/2151298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frölich J. C., Wilson T. W., Smigel M., Oates J. A. A competitive protein binding assay specific for prostaglandin E. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 29;348(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN K., SAMUELSSON B. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS: XIX. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF PROSTAGLANDINS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:117–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström E., Samuelsson B. The structure of a urinary metabolite of prostaglandin F2a in man. J Am Chem Soc. 1969 Jun 4;91(12):3398–3400. doi: 10.1021/ja01040a067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gréen K., Granström E., Samuelsson B., Axen U. Methods for quantitative analysis of PGF2 , PGE2, 9 , 11 -dihydroxy-15-keto-prost-5-enoic acid and 9 , 11 , 15-trihydroxy-prost-5-enoic acid from body fluids using deuterated carriers and gas chromatography--mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):434–453. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90373-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gréen K. The metabolism of prostaglandin F2-alpha in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 4;231(3):419–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M. Biosynthesis of prostaglandins in the renal medulla of rabbit. FEBS Lett. 1969 Oct 21;5(2):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. On the metabolism of prostaglandins E 1 and E 2 in man. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6713–6721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe B. M., Behrman H. R., Parker C. W. Radioimmunoassay measurement of prostaglandins E, A, and F in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):398–405. doi: 10.1172/JCI107196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvenaz G. H., Nugteren D. H., van Dorp D. A. Gas chromatographic determination of nanogram amounts of prostaglandins E and F. Prostaglandins. 1973 Feb;3(2):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(73)90085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonigro A. J., Itskovitz H. D., Crowshaw K., McGiff J. C. Dependency of renal blood flow on prostaglandin synthesis in the dog. Circ Res. 1973 Jun;32(6):712–717. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.6.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magotteaux G., Deby C., Barac G. Urinary elimination of smooth muscle-acting prostaglandins in the dog. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1971 Oct;79(4):799–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OATES J. A. Measurement of urinary tryptamine, tyramine and serotonin. Methods Med Res. 1961;9:169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz A. Interaction of prostaglandins with blood plasma proteins. Comparative binding of prostaglandins A 2 , F 2 and E 2 to human plasma proteins. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):631–636. doi: 10.1042/bj1300631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMUELSSON B. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS. 28. METABOLISM OF PROSTAGLANDIN E1 IN GUINEA PIG LUNG: THE STRUCTURES OF TWO METABOLITES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4097–4102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M. J., Smith J. B., Ingerman C., Kocsis J. J. Human blood prostaglandins: formation during clotting. Prostaglandins. 1972 Jun;1(6):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C., Harper M. J. Relationship between endotoxin-induced abortion and the synthesis of prostaglandin F. Prostaglandins. 1972 Mar;1(3):191–203. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smigel M., Frölich J. C., Fleischer S. Characterization of prostaglandin E receptor in membranes and its use in the assay of prostaglandin E. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:109–123. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Willis A. L. Formation and release of prostaglandins by platelets in response to thrombin. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;40(3):545P–546P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splawinski J. A., Nies A. S., Sweetman B., Oates J. A. The effects of arachidonic acid, prostaglandin E2 and prostaglandin F2alpha on the longitudinal stomach strip of the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Dec;187(3):501–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetman B. J., Frölich J. C., Watson J. T. Quantitative determination of prostaglandins. Prostaglandins. 1973 Jan;3(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(73)90139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetman B. J., Watson J. T., Carr K., Oates J. A., Frolich J. C. Quantitative vapor-phase analysis of prostaglandin F2 in female human urine. Prostaglandins. 1973 Mar;3(3):385–387. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(73)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. T., Pelster D. R., Sweetmen B. J., Frolich J. C., Oates J. A. Display-oriented data system for multiple ion detection with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in quantifying biomedically important compounds. Anal Chem. 1973 Oct;45(12):2071–2078. doi: 10.1021/ac60334a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


