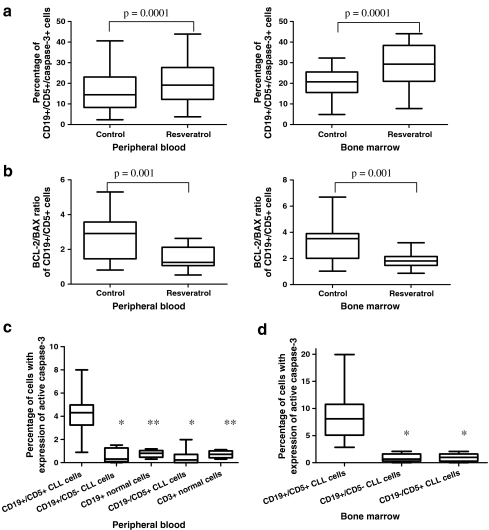
Fig. 1.
a Percentage of apoptotic leukemic cells in 24-h cultures with resveratrol in samples of peripheral blood and bone marrow. Statistically significant differences are indicated. b BCL-2/BAX ratio of CD19+/CD5+ cells in cultures treated with resveratrol for 24 h compared to the control 0-h culture. A decreased ratio was detected in resveratrol-induced cultures after 24 h. Statistically significant differences are indicated. c Percentage of apoptotic cells in populations of non-leukemic B (CD19+/CD5−) and T (CD19−/CD5+) cells from the chosen CLL patients (n = 9) and healthy donors (n = 5) in comparison to a population of leukemic CD19+/CD5+ cells in ex vivo peripheral blood cultures treated with resveratrol. Data represent the drug-induced increase in the percentage of apoptotic cells above the respective values observed in control cultures of the same cell population. Single and double asterisks indicate statistically significant differences of p = 0.0001 and p = 0.002, respectively, in comparison to the CD19+/CD5+ population. d Percentage of apoptotic cells in populations of non-leukemic B and T cells from the chosen CLL patients compared to the leukemic CD19+/CD5+ cell population in ex vivo bone marrow cultures with resveratrol. Data represent the drug-induced increase in the percentage of apoptotic cells above the respective values observed in control cultures of the same cell population. Asterisk indicates statistically significant differences of p = 0.0001 in comparison to the CD19+/CD5+ population. Graphs represent the median ± minimum/maximum