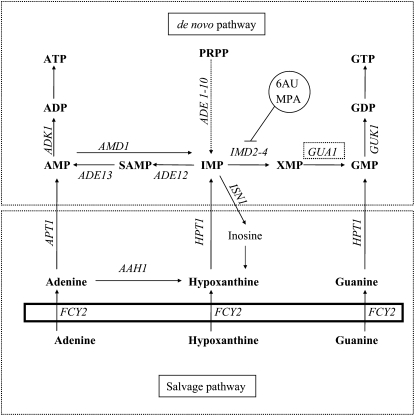
Figure 1.—
Pathways of purine nucleotide biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cytosolic reactions are shown over a rectangle representing the plasmatic membrane. The de novo pathway to synthesize IMP from PRPP involves 10 enzymatic reactions that are catalyzed by the products of the ADE 1–10 genes. The gene products of ADE12 and ADE13 catalyzed the production of AMP from IMP, and the products of IMD2/3/4 and GUA1 the synthesis of GMP from IMP. The salvage pathway involves three reactions that produce IMP, GMP, and AMP directly from their nonphosphorylated precursors, and adenine is converted to hypoxanthine by the Aah1 enzyme. The reaction products are indicated in bold font: ADP, adenosine-5′-diphosphate; AMP, adenosine-5′-monophosphate; ATP, adenosine-5′-triphosphate; GDP, guanosine-5′-diphosphate; GMP, guanosine-5′-monophosphate; GTP, guanosine-5′-triphosphate; IMP, inosine-5′-monophosphate; PRPP, 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate; SAMP, S-adenosine-5′-monophosphate; XMP, xanthosine-5′-monophosphate. Genes indicated in italics encode the following enzymatic activities: ADE12, adenylosuccinate synthetase; ADE13, adenylosuccinate lyase; ADK1, AMP kinase; AMD1, AMP deaminase; APT1, adenine phosphoribosyltransferase; FCY2, purine cytosine permease; GUK1, GMP kinase; HPT1, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase; and IMD2, IMD3, and IMD4, IMP dehydrogenase. GUA1, GMP synthetase.