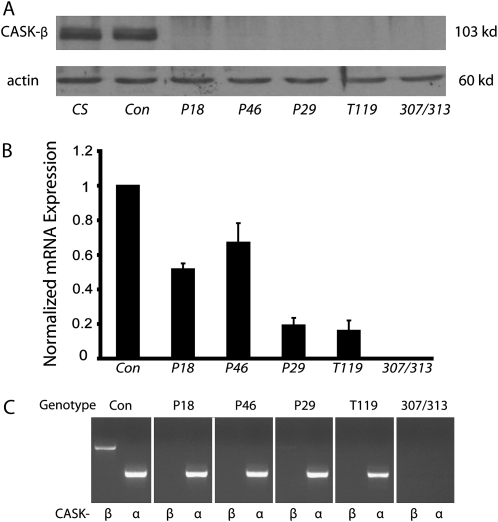
Figure 1.—
Characterization of CASK mutants. (A) Immunoblot of candidate P-element excision lines shows that lines P18, P29, P46, and T119 appear to be null for CASK-β protein, while the precise excision control line (labeled as Con) has wild-type (CS) levels of the protein, consistent with a precise excision of the P element. 307/313 is shown as a negative control, and actin normalization was used as a loading control for all samples. (B) Quantitative real-time PCR with primers specific to the distal part of the CASK transcript shows relative mRNA expression (normalized to RP49). A clear reduction of mRNA levels can be seen in all four candidate mutants, while no mRNA is seen in 307/313 flies. (C) RT-PCR was performed on cDNA using primers specific for either the CASK-α or the CASK-β isoform. Lines P18, P46, and T119 have no expression of CASK-β, while line P29 has a small amount of transcript (compared with control levels). All four mutants express the CASK-α mRNA.