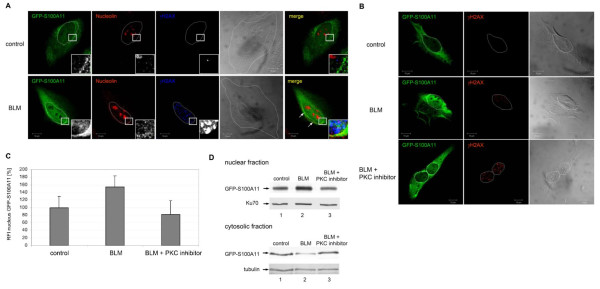
Figure 3.
Nucleolin distribution during nuclear translocation of S100A11 in DNA damaged cells. (A) U-2 OS cells which expressed GFP-S100A11 were treated with BLM to induce DSB for 1 h followed by immuno-staining against GFP-S100A11 (green), nucleolin (red) and γH2AX (blue). The overlay image (merge) shows that GFP-S100A11 and nucleolin partially colocalize in the perinuclear region (labeled by arrows) in cells containing damaged DNA compared to control cells. Areas marked by a rectangle are shown enlarged in each image as insets. (B) Inhibition of phosphorylation of S100A11 by a myristolated PKC inhibitor interferes with S100A11 translocation. U-2 OS cells were transfected with a GFP-S100A11 construct and treated with BLM for 30 min or pre-treated with a PKC inhibitor for 17 hrs and subsequently with BLM. Cells were analyzed by two-color immunostaining followed by laser scanning microscopy for GFP-S100A11 (green) and γH2AX (red). (C) Quantification of the GFP-S100A11 relative fluorescence intensity (RFI) in nuclei of cells treated with BLM or BLM and a PKC inhibitor and in control cells by assessment of the GFP-S100A11 fluorescence intensity in several nuclear areas (2 μm diameter) in percent. At least 14 cells for each condition were analyzed for quantification. Data are displayed as mean values (±SD). The average of the GFP-S100A11 fluorescence intensity measured in the control approach was set as 100%. (D) U-2 OS cells which expressed GFP-S100A11 were treated with BLM or with both BLM and the myristoylated PKC inhibitor. Afterwards, cytoplasmic as well as nuclear cell extract of treated cells and, as control, untreated cells were prepared and subjected to immunoblotting using a specific antibody against S100A11. As control for equal protein loading immunoblotting against nuclear protein Ku70 or cytosolic actin using specific antibodies were carried out.