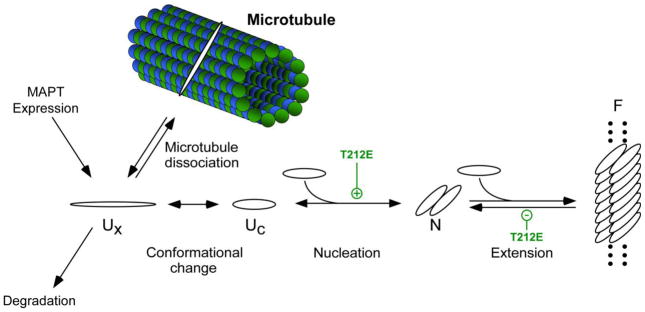
Fig. 7. Effect of T212E mutation on the tau fibrillization pathway.
Normal tau binds tightly to microtubules but dissociates upon phosphorylation to form free tau, which exists as a natively disordered, assembly incompetent monomer (Ux). A conformational change to an assembly competent state accelerates polymerization (Uc). Once assembly competent species form, the rate-limiting step in tau fibrillization is formation of dimer, which represents the thermodynamic nucleus (N). Following nucleation, extension occurs through further addition of assembly competent monomers to the filament (F) ends. Introduction of negative charge at residue T212 in the form of pseudophosphorylation, and potentially phosphorylation, affects multiple points in the pathway. See text for details.