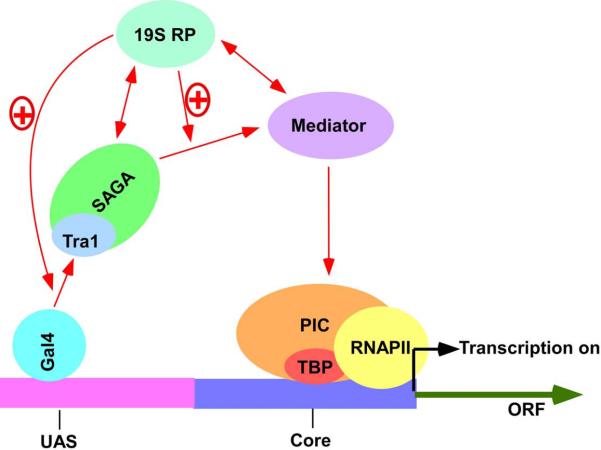
Figure 2.
A model showing the role of the 19S RP in regulation of transcriptional activation of the GAL1 genes in vivo. The activator, Gal4p recruits SAGA to the GAL1 UAS through its interaction with Tra1p [27]. However, the targeting of SAGA to the GAL1 UAS is less efficient in the absence of the 19S RP [210]. The ATPase activity of the 19S RP enhances SAGA targeting to the GAL1 UAS in a positive feedback manner [210]. Similar enhancement of SAGA targeting has also been demonstrated by biochemical studies [207]. The 19S ATPase activity is also essential for recruitment of the Mediator complex [210]. Mediator is required for formation of the PIC [27]. Further, in support of this model, several interactions have been demonstrated by biochemical and genetic studies [126, 127, 207, 211–213, 221]. For example, Lee et al. [207] have shown the physical and genetic interaction between SAGA and 19S RP. Sun et al. [221] have demonstrated the physical interaction between Mediator and the 19S RP. Functional and genetic interactions between SAGA and Mediator have also been reported [126, 127]. Further, several biochemical studies have shown the physical interaction of the 19S RP with the components of the PIC [211–213]. However, whether these interactions occur directly in vivo remains to be investigated. “+” referes “stimulation”.