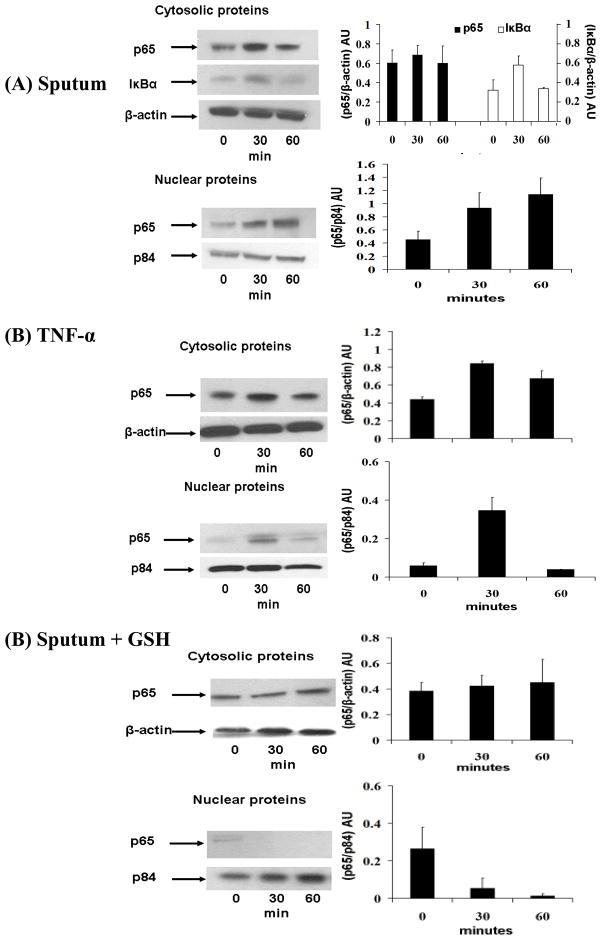
Figure 7. GSH inhibits CF sputum-induced NF-κB activation.
HBE1 cells were starved of growth factors and treated with CF sputum (sol-phase) (10 μl/ml of media). Nuclear and cytosolic protein fractions were extracted at 0, 30 and 60 minutes. NF-κB activation was analysed by western blot assay. (A) Nuclear translocation of NF-κB subunit, p65 and degradation of cytosolic IκB-α suggesting CF sputum (sol-phase) mediated NF-κB activation. β-actin and p84 served as loading controls for cytosolic and nuclear protein fractions respectively. (B) Nuclear translocation of p65 in TNF-α treated (20 μg/ml) HBE1 cells which served as controls. (C) HBE1 cells when treated with CF sputum (sol-phase) along with GSH (1 mM) did not show p65 nuclear translocation suggesting inhibition of NF-κB activation. The blots shown are a representative of 3 independent experiments. Densitometric analysis was performed for each blot, and the quantitative data illustrated in graphs to the right of the figure.