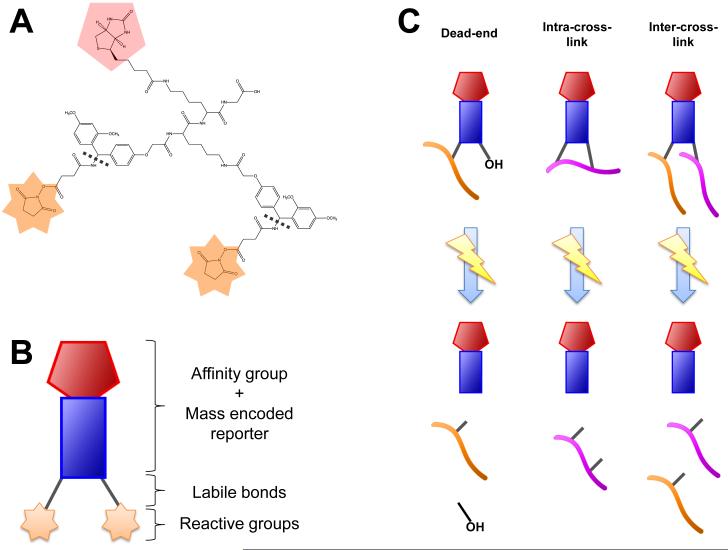
Figure 1.
Illustration of PIR cross-linking technology. (A) The chemical structure for the in-house synthesized cross-linker, Brink. Shown in (B) is a cartoon illustration of Brink, highlighting the affinity group and mass encoded tag, the labile bond regions, and the reactive groups. (C) Three general PIR products are formed from the fragmentation of PIR-linked peptides: dead-end, intra-cross-links, and inter-cross-links. Dead-ends and intra-cross-linked relationships are made from the contribution of a single peptide mass and the reporter ion mass. Inter-cross-linked relationships involve two peptide ions and the reporter ion.