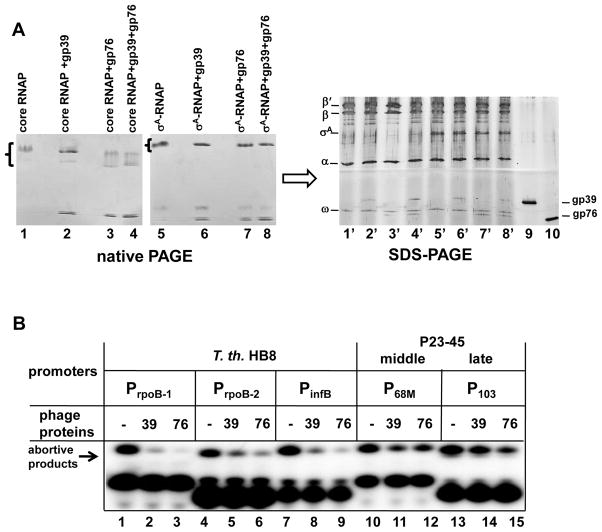
Figure 9. The P23-45 phage proteins gp39 and gp76 bind to T. th. HB8 RNAP and inhibit transcription initiation from host promoters but not from middle and late phage promoters.
A. Gp39 and gp76 bind to both core RNAP and RNAP-σA holoenzyme. The proteins alone or together were incubated with RNAP core (lanes 2–4) or with RNAP-σA holoenzyme (lanes 6–8) and analyzed by native gradient PAGE. Next, the native gels were stained with Coomassie stain, and the bands due to proteins (indicated by brackets in Fig. 9A) were excised from the gels and their composition were determined by denaturing SDS-PAGE (lanes 1′-8′). Gp39 and gp76 were loaded as markers (lanes 9 and 10, respectively).
B. The results of abortive transcription initiation by T. th. HB8 RNAP-σA holoenzyme at several representative host T. th. HB8 (lanes 1–9) and middle/late phage (lanes 10–15) promoters in the presence or absence of either gp39 or gp76 are shown.