Table 2.
Presentation, imaging and suggested treatment in PGL by hereditary backgrounds.
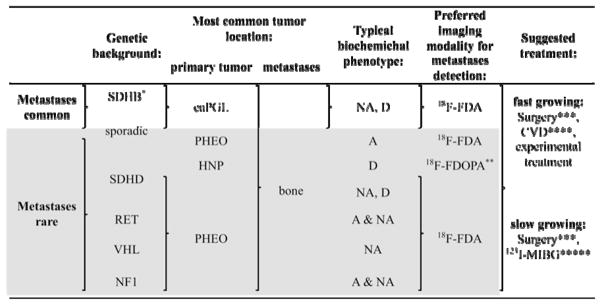 |
Abbreviations: adrenergic (A) (elevated epinephrine (Epi) and/or metanephrine (MN)); noradrenergic (NA) (elevated norepinephrine (NE) and/or normetanephrine (NMN)); dopaminerg (D) (elevated dopamine (DA); L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) and/or methoxytyramine); adrenal PGL (PHEO); extra-adrenal PGL (eaPGL); head and neck PGL (HNP).
Risk of metastatic disease particularly high in children and adolescents.
Mainly studied on primary HNP but potentially similarly effective for metastases.
Complete resection of metastases is rarely possible, but resection can have a good palliative effect (avoidance of further organ or bone destruction by tumor growth as well as reduction of catecholamine levels which leads to a decrease in related signs and symptoms).
own unpublished observations suggest that (at least) patients with SDHB related fast growing tumors initially respond well. Physicians are recommended not to stop CVD, because resumption of therapy almost always results in chemotherapy resistant tumors (if toxicity occurs, longer intervals between cycles or a reduced dosage can be used).
High doses may be effective 111, however, additional studies and long-term observations are needed.
