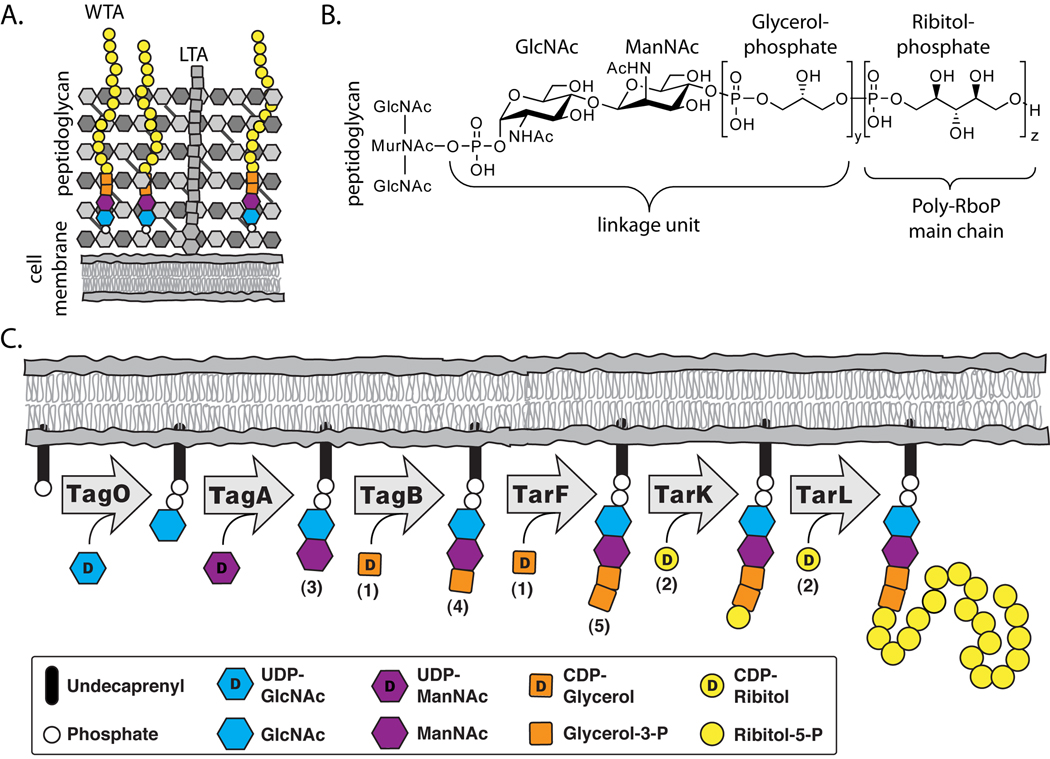
Figure 1. Teichoic acids are a major component of the gram-positive cell wall and the pathway for ribitol-phosphate wall teichoic acids has been proposed.
(A) A schematic of the Gram-positive cell wall depicting membrane anchored lipoteichoic acid and peptidoglycan anchored wall teichoic acid (WTA) polymers.
(B) The chemical structure of ribitol-phosphate wall teichoic acid as found in S. aureus and B. subtilis W23 (y = 1–2, z = 20–40). The tailoring modifications on the main chain hydroxyls are omitted for clarity.
(C) Lazarevic et al. (2002) proposed the biosynthetic pathway depicted above for polyribitol-phosphate WTAs. The numbers in parentheses correspond to the substrates utilized in our in vitro experiments (see Figure 2 for chemical structures).