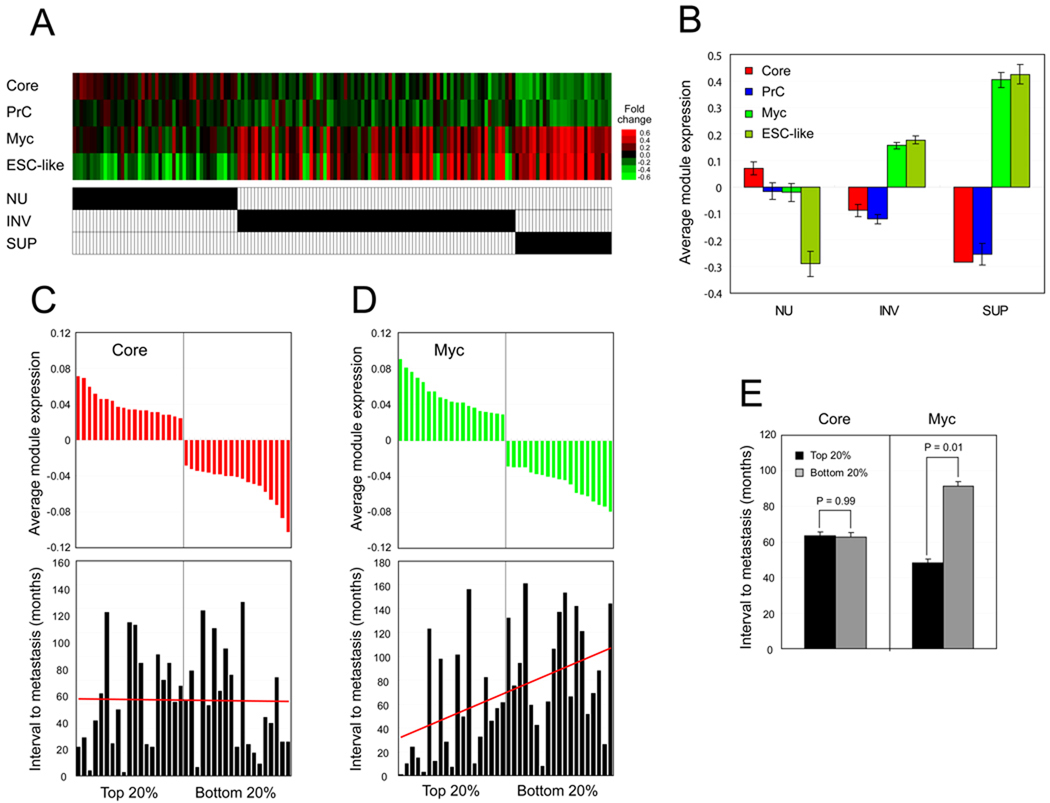
Figure 7. ES cell modules in human cancers.
(A–B) Average gene expression values (log2) of ES cell modules and previously defined ESC-like module are tested in human bladder carcinoma samples including superficial (SUP), and invasive carcinomas (INV), as well as normal urothelium (NU) as a control group (marked by black bars) (Sanchez-Carbayo et al., 2006). Each column represents one patient sample (total 157 samples) (A). Averaged module activities within the sample group (NU, INV, and SUP) (B). Data represented as mean ± SEM.
(C–E) Average gene expression values (log2) of ES cell Core (C) and Myc (D) module are tested from 97 human breast cancer patient samples (van 't Veer et al., 2002). (C) Core module activities were calculated, and top and bottom 20% of samples (19 samples each) were further analyzed. Bar graph represents the corresponding interval to metastases (months, bottom panel). (D) Samples showing top and bottom 20% of Myc module activity were further analyzed. Bar graph represents the corresponding interval to metastases (months) for each patient (bottom panel). (E) For each tested group (C–D), interval to distant metastases is calculated as mean ± SEM, and p-values are from Student’s T-tests. See also Figure S5.