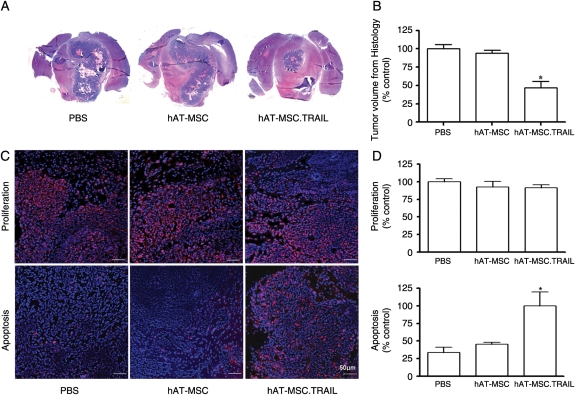
Fig. 4.
Short-term therapeutic efficacy of hAT-MSC.TRAIL in vivo. (A) Representative histological images (H&E staining; magnification, ×1) (A). A 56.3% decrease in tumor volume was observed in hAT-MSC.TRAIL–treated animals compared with PBS-treated animals (P < .001; Kruskal–Wallis test) (B). Representative immunofluorescence images. Primary antibodies included anti-Ki67 nuclear antigen (for the detection of proliferating cells; red color) and anticleaved caspase-3 (for the detection of apoptosis; red color) (C). Sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Bars indicate 50 μm. Immunofluorescence analysis revealed that the proliferative indices were not different among the groups. In contrast, the number of apoptotic cells was increased 3.01-fold in the hAT-MSC.TRAIL-treated group compared with the control groups (P < .05; Kruskal–Wallis test) (D).