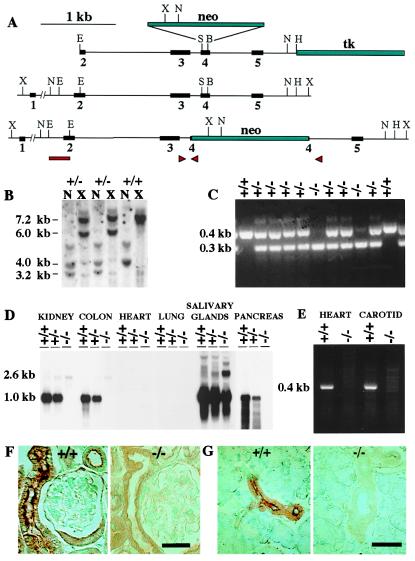
Figure 1.
Targeted disruption of the mouse tissue kallikrein gene. (A) The targeting construct containing the neomycin-resistance gene (neo) and the herpes simplex virus/thymidine kinase gene (tk) is shown next to the wild-type and targeted alleles. X, XbaI; N, NcoI; E, EcoRI; S, SacI; B, BsgI; H, HindIII. (B) Southern analysis of genomic DNA from wild-type (+/+) and targeted (+/−) embryonic stem cells with a probe overlapping intron 1 and exon 2 (bar) reveals different NcoI (3.2 versus 4.0 kb) and XbaI (6.0 versus 7.2 kb) fragments in the targeted cells. (C) PCR analysis of tail DNA from wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/−), and homozygous (−/−) mice from offspring of a heterozygous cross, using primers in introns 3 and 4 and in the neo gene (arrowheads in A). (D) Northern analysis of total RNA (20 μg per lane) from pooled tissues of five +/+, five +/−, and five −/− mice. The blot was hybridized with a mouse tissue kallikrein cDNA probe spanning exons 2 and 3, and was exposed for 6 h. (E) Detection of tissue kallikrein mRNA by RT-PCR in the heart and carotid of +/+ mice. The reactions were performed with primers situated in exons 2 and 4, using the same RNA pools that had been used for Northern analysis. The identity of the 0.4-kb band detected in +/+ mice was confirmed to be tissue kallikrein by direct sequencing. (F) Immunostaining of tissue kallikrein in the kidneys. The labeling in +/+ mice is localized in the apical membrane of connecting tubular cells. (G) Immunostaining of tissue kallikrein in the salivary glands. The labeling in +/+ mice is found in the apical membrane of the epithelial cells lining the excretory ducts. (Bars = 20 μm.)