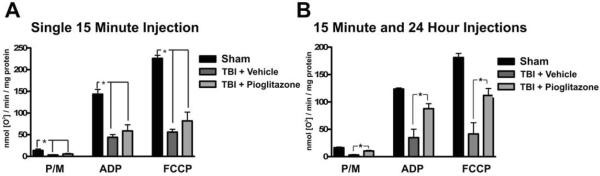
Figure 1. Pioglitazone treatment attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction after TBI.
In order to assess the ability of Pioglitazone to prevent the mitochondrial dysfunction which occurs with this model of TBI, mitochondrial bioenergetic function was analyzed 1 day following a controlled cortical impact TBI. A. Following a single injection of Pioglitazone (10mg/kg) 15 minutes after the injury, no improvements in mitochondrial function were observed. B. When Pioglitazone was administered at both at 15 minutes and 24 hours after the injury (10mg/kg/injection) a significant increase in mitochondrial bioenergetics was observed. These studies indicate that treatment with Pioglitazone at 15 minutes and 24 hours is capable of preventing mitochondrial dysfunction following TBI.
(* p<0.01 by one-way ANOVA with SNK post-test).