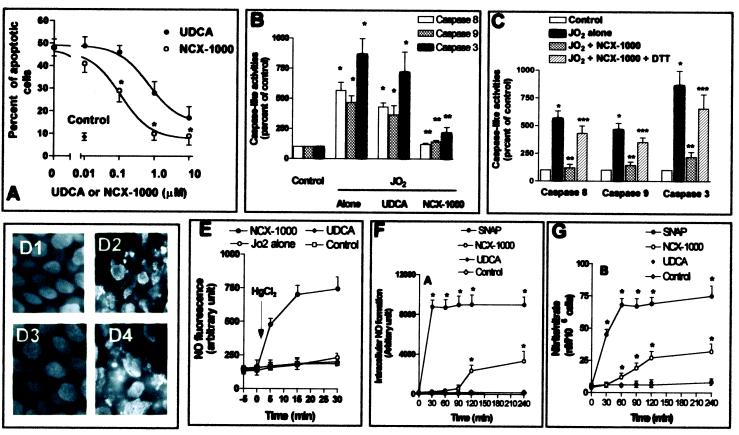
Figure 4.
NCX-1000 protects HepG2 cells from Jo2-induced apoptosis. (A) UDCA and NCX-1000 causes a concentration-dependent inhibition of Jo2-induced apoptosis. Data are mean ± SE of six experiments carried out in duplicate. *, P < 0.01 versus Jo2 alone. (B) NCX-1000 inhibits caspase 3, 8, and 9 activity in HepG2 cells treated with Jo2. Data are mean ± SE of six experiments carried out in duplicate. *, P < 0.01 versus control; **, P < 0.01 versus Jo2 alone. (C) Reversibility of caspase inhibition by DTT. Data are mean ± SE of six experiments carried out in duplicate. *, P < 0.01 versus control; **, P < 0.01 versus Jo2 alone; ***, P < 0.01 versus Jo2 plus NCX-1000. (D) 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole staining of HepG2 nuclei. D1, control cells; D2, cells treated with Jo2. Note extensive nuclear fragmentation. D3, cells treated with Jo2 + 10 μM NCX-1000; D4, cells treated with Jo2 + 10 μM UDCA. (E) Release of NO from cell lysates incubated with NCX-1000. Data are mean ± SE of six experiments carried out in duplicate. (F and G) Time course of intracellular NO formation and nitrite/nitrate release from HepG2 cells incubated in the absence of added agent (control) or 100 μM of SNAP, UDCA, or NCX-1000. Data are mean ± SE of six different experiments. *, P < 0.01 versus baseline.