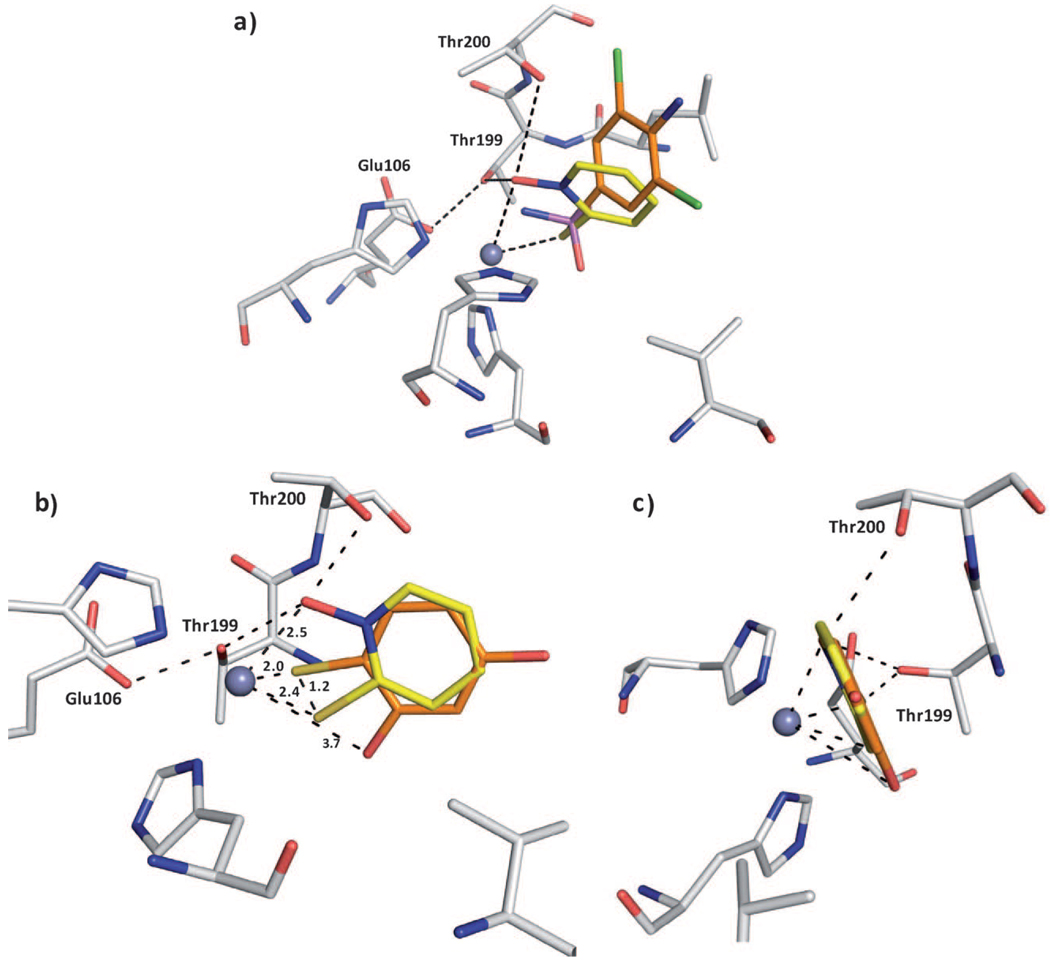
Figure 3.
Superpositions of compound 4. a) Superposition with sulfonamide inhibitor 5 in complex with CA II; the protein residues and ligands are shown in stick representation (protein:  ; compound 4:
; compound 4:  ; sulfonamide 5:
; sulfonamide 5:  ; PDB ID: 1ZGE). The sulfur atoms are located at different positions. Fragment 4 forms an additional coordination to the Zn2+ ion. The ring system of 4 is shifted relative to the sulfonamide inhibitor which is dependent on the hydrogen bonds of 4 to the oxygen atoms of Thr199 and Thr200. b) Superposition of 4 with a structurally related fragment 7 from a crystal structure PDB ID: 2OSF (
; PDB ID: 1ZGE). The sulfur atoms are located at different positions. Fragment 4 forms an additional coordination to the Zn2+ ion. The ring system of 4 is shifted relative to the sulfonamide inhibitor which is dependent on the hydrogen bonds of 4 to the oxygen atoms of Thr199 and Thr200. b) Superposition of 4 with a structurally related fragment 7 from a crystal structure PDB ID: 2OSF ( ). The sulfur atoms are shifted by 1.2 Å. The ring system of the superimposed ligands is rotated by 180°. In contrast to this ligand, 4 can form hydrogen bonds to Thr199 and Thr200. c) Image in panel b) rotated by 90°.
). The sulfur atoms are shifted by 1.2 Å. The ring system of the superimposed ligands is rotated by 180°. In contrast to this ligand, 4 can form hydrogen bonds to Thr199 and Thr200. c) Image in panel b) rotated by 90°.