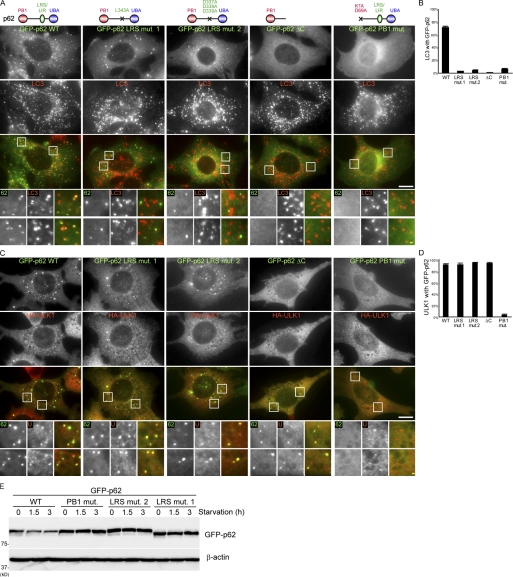
Figure 4.
The PB1 domain but not LRS of p62 is essential for localization to the autophagosome formation site. (A and B) p62 KO MEFs stably expressing GFP-p62 wild type, GFP-p62 LRS mutant 1 (L343A), GFP-p62 LRS mutant 2 (D337A, D338A, and D339A), GFP-p62ΔC (1–265 amino acids), and PB1 mutant (K7A and D69A) were cultured in starvation medium for 1 h. Cells were analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy using anti-LC3 antibodies. GFP-p62 positivity (%) of the LC3 puncta is shown in B. Data represent mean ± SEM of 30 images. (C and D) p62 KO MEFs stably coexpressing HA-ULK1 and one of the GFP-p62 described in A were cultured in starvation medium containing 0.2 µM wortmannin for 1 h. Cells were analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy using anti-HA antibodies. GFP-p62 positivity (%) of the LC3 puncta is shown in D. Data represent mean ± SEM of 30 images. (E) p62 KO MEFs stably expressing the indicated GFP-p62 were cultured in regular or starvation medium for 1.5 and 3 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblot analysis with the anti-p62 and β-actin antibodies. Signal color is indicated by color of typeface. St. M., starvation medium; WM, wortmannin; WT, wild type. Bars: (white) 10 µm; (yellow) 1 µm.