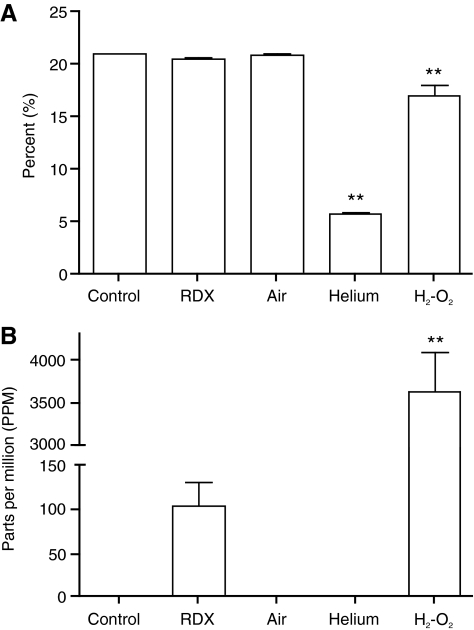
FIG. 8.
Gas content following blasts. Oxygen (A) and carbon monoxide (B) levels within the McMillan blast device were measured following blasts of approximately 120 kPa. There was a substantial decrease in oxygen levels following helium-driven blasts, and a more modest decrease following oxyhydrogen-driven blasts. Carbon monoxide levels were greatly elevated following oxyhydrogen-driven blasts, as a result of combustion of the polyethylene bag used to contain the gases prior to detonation. The slight increase in carbon monoxide seen following RDX-driven blasts was not statistically significant, but is also thought to result from combustion of the latex and electrical tape used to secure the RDX prior to detonation. Error bars represent standard deviation from the mean (**p < 0.01, n = 3; cyclotrimethylenetrinitramine; H2-O2, oxyhydrogen).