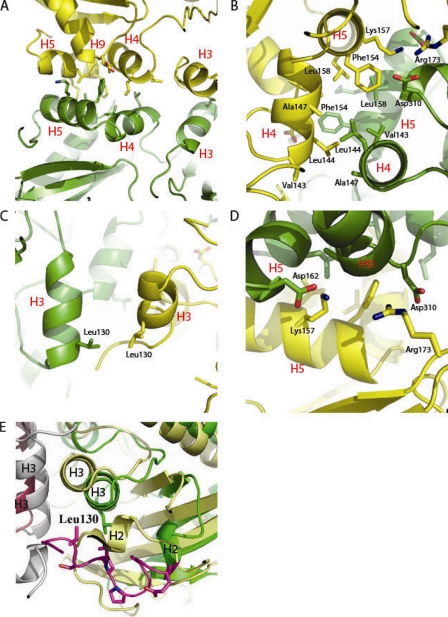
FIG. 4.
Ddl dimer interface. (A) Helix packing at the dimer interface. H5, H9, and H4 all pack against their dimer partners. H4 packs against the dimer partner H4 at an offset of almost 180o, and H5 packs against the dimer partner H5 at a similar offset. (B) Hydrophobic cleft of the dimer interface. Residues Leu158, Phe154, Ala147, Leu144, and Val143 all form hydrophobic interactions at the dimer interface. (C) Hydrophobic packing of H3/H3 via residue Leu130. (D) Electrostatic interactions at the dimer interface. Arg173 forms an electrostatic interaction with Asp310, and Lys157 forms an electrostatic interaction with Asp162. (E) Superimposition of M. tuberculosis Ddl (monomer A in green ribbons and monomer B in gray ribbons) with S. aureus Ddl (monomer A in yellow ribbons and monomer B in magenta ribbons) (PDB accession code 2I87), with the M. tuberculosis-specific insertion shown in purple (25). The M. tuberculosis-specific insertion allows for shifts in helices 2 and 3 away from the dimer interface compared to the levels for the S. aureus structure.