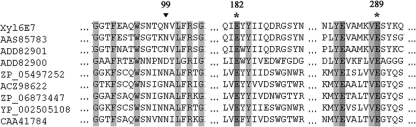
FIG. 2.
Alignment of Xyl6E7 with eight of its most related GH11 xylanases. The protein reported under GenBank accession no. AAS85783 was derived from caterpillar gut, those under accession no. ADD82901 and ADD82900 were derived from termite gut, that under accession no. ZP_05497252 was from Clostridium papyrosolvens, that under accession no. ACZ98622 was from Cellulosilyticum ruminicola, that under accession no. ZP_06873447 was from Bacillus subtilis subsp. spizizenii ATCC 6633, that under accession no. YP_002505108 was from Clostridium cellulolyticum H10, and that under accession no. CAA41784 was from Bacillus sp. strain YA-335. Multiple-sequence alignments were performed with ClustalW. Identical residues are shaded in black. The two highly conserved catalytically essential glutamic acid residues of GH11 xylanases are marked by asterisks, and the residue known to be responsible for the pH dependence of GH11 xylanases is marked by a triangle.