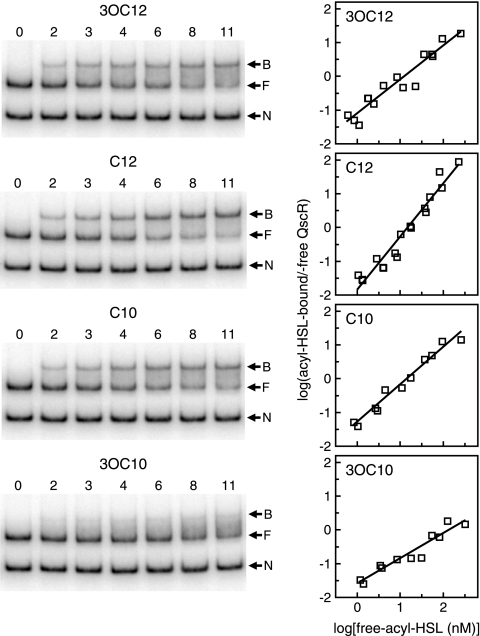
FIG. 6.
Estimation of the binding affinities of QscR for different acyl-HSLs. EMSAs were performed with a fixed amount of 3OC6-HSL-QscR (5 nM). The different acyl-HSLs were added at different concentrations as indicated. Assays were performed two or three times for each acyl-HSL. (Left) Representative EMSA results. The numbers above the lanes are acyl-HSL concentrations (in nanomolar concentrations). The negative control (lanes 0) contained no QscR. The positions of nonspecific DNA (N), QscR-free target DNA (F), and QscR-bound DNA (B) are indicated by the arrows to the right of the gels. (Right) Hill plots derived from two or three independent data sets for each acyl-HSL. The amount of QscR-bound target DNA was calculated as the intensity of the free target DNA in the control lane (no QscR added) minus free target DNA in the lane of interest. The amount of acyl-HSL-bound QscR in each reaction mixture was then estimated from the amount of band shifting by using the fitted lines of the Hill plots in Fig. 5As standard curves. The numbers indicated on the x axis are logarithms of QscR-free acyl-HSL concentrations, which were calculated as the amount of total acyl-HSL added in each reaction mixture minus the estimated amount of signal-bound QscR.