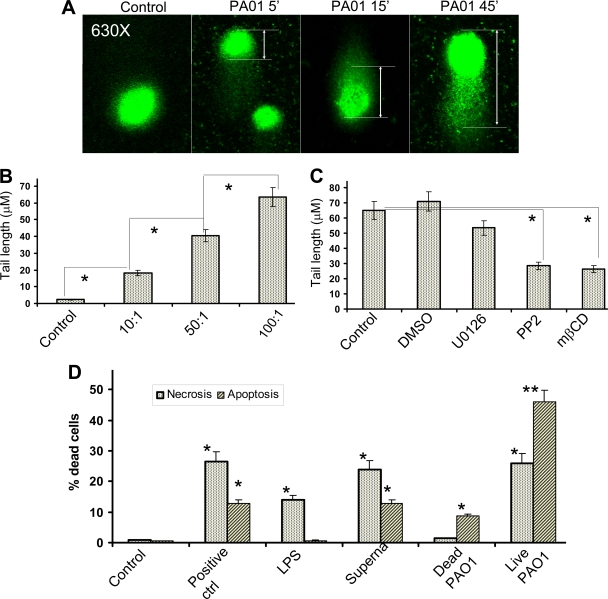
FIG. 1.
Induction of DNA damage and cell death by PAO1. (A) Time-dependent DNA damage. A549 cells were infected with PAO1 (MOI, 10:1) for various durations, and DNA damage was determined by comet assay after rewinding the DNA with alkaline buffer. Slides were stained with SYBR and viewed using fluorescence microscopy (see Materials and Methods). The control contained no bacteria. (B) Bacterial load-dependent DNA damage. A549 cells were infected with various amount of PAO1 for 1 h, and tail lengths (indicated by rulers) were measured by CometScore software (100 cells counted/sample) (*, P < 0.05, confidence interval [CI] 95%). The x axis shows various MOIs. (C) Reduction of DNA damage by blocking Lyn kinase (PP2, 5 nM) and lipid rafts (mβCD, 10 mM) as determined by comet assay. However, the vehicle (DMSO at 5 nM as a dilution reagent) and MEK-ERK1/2 inhibitor (U0126, 2.5 μΜ) had no effects on PAO1-induced DNA damage. In addition, PP2 and mβCD alone had no effects on tail lengths compared to the control (not shown). (D) Quantitative assays of apoptosis and necrosis. LPS (serotype 10, 200 ng/ml), supernatant of PAO1, and live PAO1 were incubated with AECII cells for 1 h, and the bacteria and reagents were replaced with fresh medium containing antibiotics. Hydrogen peroxide (100 μM) served as the positive control (ctrl) for necrosis and apoptosis. The cells were further incubated for 18 h and assessed by Vybrant assay (one-way ANOVA; *, P < 0.05, CI 95%; **, P < 0.01, CI 99% [all compared to the control]). The data shown are representative of three experiments.