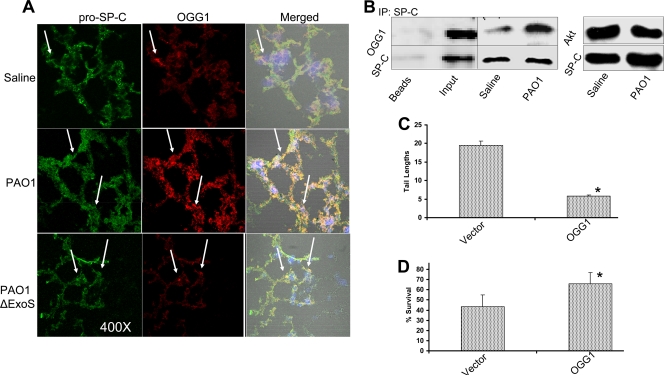
FIG. 3.
PAO1-induced OGG1 expression in AECII cells. (A) OGG1 expression in lung AECII cells as identified by indirect immunofluorescence. Cryosections of mouse lungs infected with PAO1 for 18 h were stained with antibodies against OGG1 (red) or pro-SP-C (green) (each staining and colocalization indicated with arrows). (B) Identification of specific OGG1 expression in AECII cells by coimmunoprecipitation (IP). Isolated AECII cells from female C57BL/6 mice were infected with PAO1, and cell lysates were pulled down with pro-SP-C antibodies and probed with anti-OGG1 or anti-pro-SP-C antibodies (the control was AECII cells from untreated mice). Pulldown with Akt antibodies showed no association between OGG1 and pro-SP-C. (C) Reduction of DNA damage after PAO1 infection by overexpression of OGG1 in A549 cells with the retroviral vector ps91-EGFP-OGG1. Cells were infected with PAO1 for 1 h, and a comet assay was used to measure the extent of DNA damage versus that in vector control cells (**, P < 0.01). (D) Protection against PAO1 infection by overexpression of OGG1 in A549 cells versus vector control cells. Proliferation of infected cells (1 h of infection and ensuing incubation without bacteria for 48 h) was determined by MTT assay, and data are expressed as percentages (*, P < 0.05). The data shown are representative of three experiments.