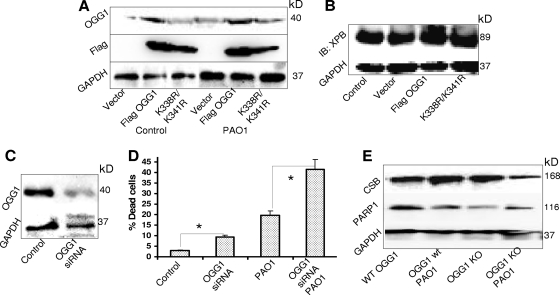
FIG. 5.
Interaction of DNA repair proteins in response to PAO1 infection. (A) Perturbation of OGG1 acetylation reduced the DNA repair response to infectious oxidation. A549 cells were transfected with a mutant FLAG-OGG1 construct with defects in acetylation sites (K338R/K341R) or with a WT FLAG-OGG1 construct. The lysates were probed with either OGG1 or FLAG antibodies. Sample loading was monitored by GAPDH. (B) Expression of XPB and OGG1 after perturbation of OGG1 acetylation sites. Cell lysates were probed with XPB and GAPDH (loading) antibodies, respectively. IB, immunoblotting. (C) Transfection of OGG1 siRNA decreased the expression of OGG1 in AECII cells. The expression of OGG1 was measured by Western blotting with antibodies against OGG1 and reprobed with GAPDH (loading control). (D) Transfection of OGG1 siRNA decreased AECII cell survival compared to that of controls (trypan blue exclusion; *, P < 0.05). (E) Loss of OGG1 reduced responses to bacterial infection by CSB and PARP1 in OGG1−/− mice versus OGG1+/+ mice (five mice per group). Lung lysates were assessed for DNA repair protein expression as indicated (Western blotting). The data shown are representative of three experiments.