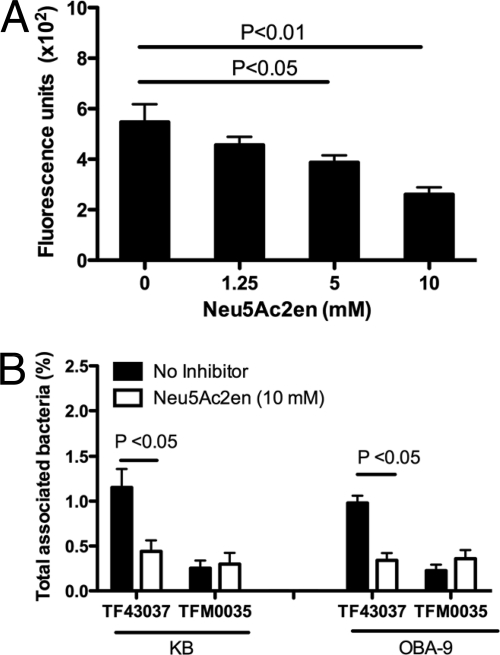
FIG. 5.
Effect of sialidase inhibitor Neu5Ac2en on epithelial cell attachment. (A) Dose-dependent inhibition of T. forsythia-associated sialidase activity by Neu5Ac2en. Triton X-100-extracted fractions from T. forsythia wild-type cells were treated with increasing concentrations of sialidase inhibitor for 30 min at 37°C. Sialidase activity was then measured with the fluorescent substrate 4-methylumbelliferyl-N-acetyl-α-d-neuraminic acid. Bars represent fluorescence values (means and standard deviations) of triplicate readings. Data are representative of more than three independent experiments with similar results. (B) Inhibition of T. forsythia wild-type attachment to epithelial cells (KB or OBA-9) by a sialidase inhibitor. T. forsythia wild-type cells were pretreated with 10 mM Neu5Ac2en for 30 min prior to incubation with epithelial cell monolayers. Monolayers with bacteria were incubated for 1 h, and bacterial attachment levels were determined as previously described. Data are representative of three (KB cells) or two (OBA-9 cells) independent experiments with similar results.