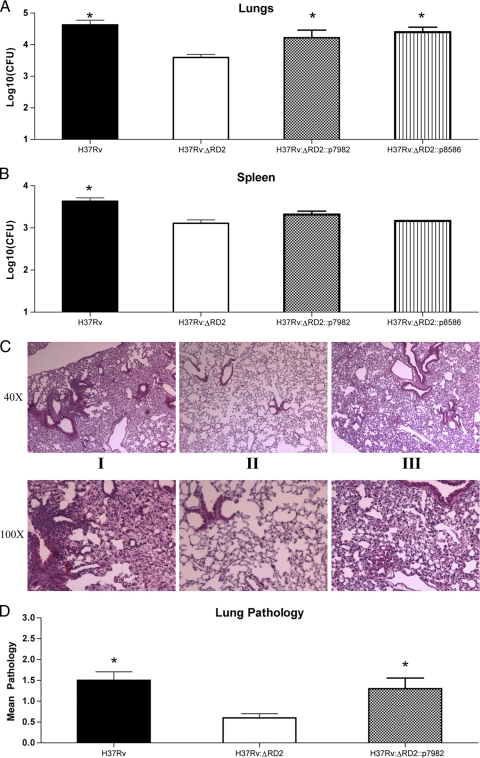
FIG. 4.
Complementation of virulence phenotype. Bacterial burden in the lungs (A) and spleen (B) at 3 weeks postinfection. Six- to 8-week-old C57BL/6 mice were infected by aerosol with H37Rv (black bar), H37Rv:ΔRD2 (white bar), H37Rv:ΔRD2::p7982 (gray bar), or H37Rv:ΔRD2::p8586 (striped bar). Data represent the means ± standard errors of the means of six mice, where an asterisk indicates P < 0.05. (C) Histology of lung lesions from infected mice with H37Rv (i), H37Rv:ΔRD2 (ii), or H37Rv:ΔRD2::p7982 (iii) at 3 weeks postinfection. Five mice per group were used and lungs were stained with H&E. Micrographs (magnification, ×40 and ×100) shown are representative lung sections from each group. (D) Average pathological scores from mice infected with H37Rv (black bar), H37Rv:ΔRD2 (gray bar), or H37Rv:ΔRD2::p7982 (gray bar) at 3 weeks postinfection. Pathology was evaluated from H&E-stained lung sections by two blinded readers and scored on a scale of 0 (absent) to 4 (very severe). Bars represent means ± standard errors of the means, where an asterisk indicates a P value of ≤0.05.