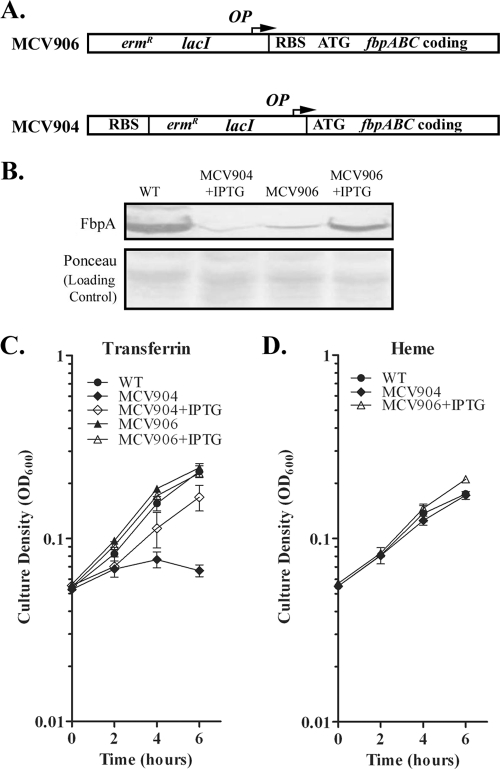
FIG. 6.
Characterization of conditional FbpABC expression strains. (A) Genetic organization of the fbpABC locus in mutant strains MCV904 and MCV906. In strain MCV906, the native promoter has been replaced by an inducible promoter (OP). In MCV904 the inducible promoter (OP) was inserted downstream of the native ribosome binding site (RBS). The arrow indicates the direction of transcription. WT, wild type. (B) FbpA expression in FA19 and the mutants that conditionally express FbpA. Strains were grown in CDM under iron-stressed conditions. Some cultures were supplemented with 2 mM IPTG (+IPTG). Gonococci were lysed, subjected to SDS-PAGE, and, following transfer of proteins to nitrocellulose, probed with a polyclonal anti-rFbpA antibody. Recombinant FbpA (rFbpA) was used as a positive control. (C) Growth with hTf by mutants that conditionally express FbpA. Strains were grown in CDM containing 2.5 μM bovine transferrin, supplemented with 7.5 μM human transferrin. MCV904 and MCV906 were grown in the presence (+IPTG) or absence of 2 mM IPTG. (D) Growth with heme by mutants that conditionally express FbpA. Strains were grown in CDM containing 2.5 μM bovine transferrin, supplemented with 4 μM heme. Each time point represents the mean and standard deviation of results from three independent experiments.