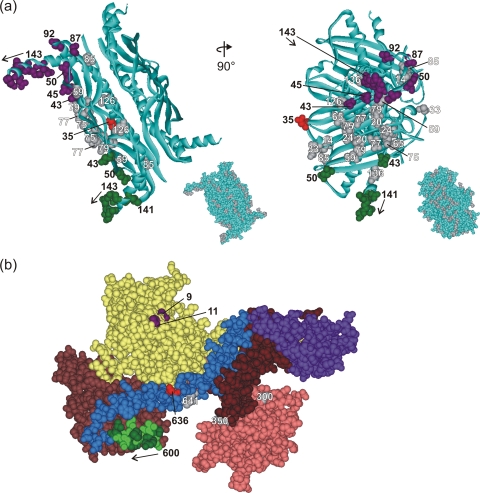
FIG. 2.
Structure of SecA and SecB. (a) Structure of tetrameric SecB in ribbon representation from Haemophilus influenzae (Protein Data Bank [PDB] code 1FX3). The Haemophilus structure is used here instead of that of E. coli SecB to illustrate the C-terminal residues 141 to 155, which are not resolved in the E. coli structure (PDB code 1QYN). The numbered CPK models of side chains are those residues used in this study. The residues that showed cross-linking are colored corresponding to the cross-linking partner in SecA. The gray residues showed no cross-linking. The inset shows SecB in CPK representation with all residues used in this study shown in gray. The images on the right correspond to a 90° rotation around the y axis of the images on the left. (b) Structure of SecA in CPK representation with the subdomains in color as described in the text. The residues that showed cross-links are shown in purple (V9 and G11), light green (601, 603, 605, 607, and 609), and red (636). The gray residues did not cross-link. Residue 827 is not shown because it lies in the IRA1 domain (brown) and is masked by the helical wing domain (purple). PDB code 2FSF with the PBD model based on the B. subtilis SecA PDB code 1TF5.