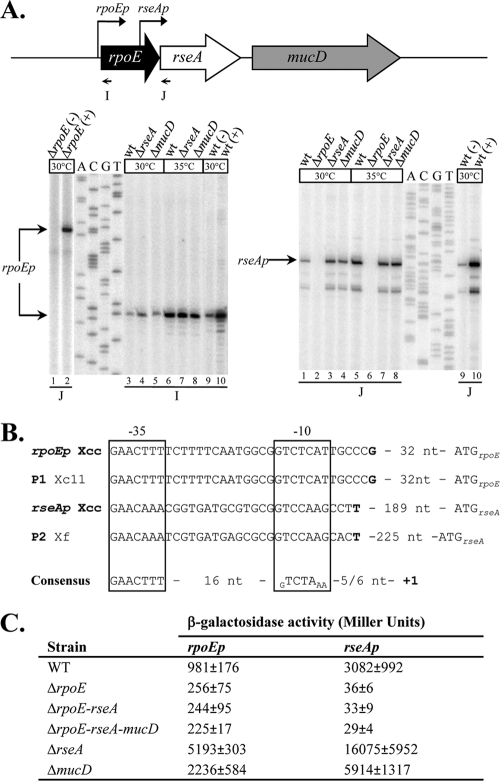
FIG. 2.
Expression of the rpoE operon genes. (A) Determination of the transcription start site of the rpoE operon genes by primer extension. The schematic (to scale) shows the primers used for transcriptional start site mapping experiments, and the black arrows indicate the positions of the two identified σE-dependent promoters. Total RNAs from the WT, ΔrpoE, ΔrseA, ΔmucD, and WT or ΔrpoE strains containing the control plasmid p917 (−) or the σE-overexpressing plasmid p917-rpoE (+) were used as templates in primer extension experiments when they were suited. Total RNAs were obtained from cells incubated at 30°C or after a 60-min shift at 35°C. The arrows indicate the bands corresponding to the observed start site. (B) Sequence alignment depicting the relevant features of rpoEp and rseAp compared to σE-binding sites of P1 of X. campestris pv. campestris strain 11 (Xc11) and P2 of X. fastidiosa (Xf) (17, 24). The transcription start sites identified by primer extension are indicated in boldface, and the putative −10 and −35 regions are boxed. The consensus ECF02 group of ECF σ factor sites is indicated below (65). (C) Determination of rpoEp and rseAp activities in different strains. Plasmids containing a transcriptional fusion of the upstream region of rpoEp or rseAp to the lacZ gene were transferred into X. campestris pv. campestris strains. Overnight cultures of these strains grown in MOKA medium were diluted in the same medium and grown for 9 h before determination of β-galactosidase activity. The results represent the mean values of at least two independent experiments, each performed in triplicate, with the standard errors.