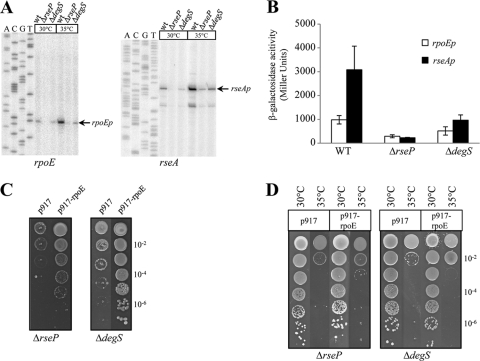
FIG. 8.
The deletion of rseP or degS impairs σE activation. (A) Expression of σE-dependent promoters using primer extension assays. Total RNA was prepared from the WT, ΔrseP, and ΔdegS mutant strains grown at 30°C or exposed to a temperature upshift at 35°C for 60 min. Primers rpoE-EXT and rseA(2)-EXT were used. (B) Determination of rpoEp and rseAp activities in WT, ΔdegS, and ΔrseP strains. Plasmids containing a transcriptional fusion of the upstream region of rpoEp or rseAp to the lacZ gene were transferred into X. campestris pv. campestris strains. Overnight cultures of these strains grown in MOKA medium were diluted in the same medium and grown for 9 h before determination of β-galactosidase activity. The results represent the mean values of at least two independent experiments, each performed in triplicate, and the error bars indicate the standard errors. (C) Influence of 40 μM cadmium on growth of X. campestris pv. campestris WT, ΔdegS, and ΔrseP strains containing control plasmid p917 or σE-overexpressing plasmid p917-rpoE. Serial 10-fold dilutions of late-exponential-phase bacteria were spotted on MOKA plates containing cadmium and incubated at 30°C for 72 h. (D) Heat sensitivities of X. campestris pv. campestris WT, ΔdegS, and ΔrseP strains containing control plasmid p917 or σE-overexpressing plasmid p917-rpoE. Serial 10-fold dilutions of late-exponential-phase bacteria were spotted on plates and incubated at 35°C for 72 h. For panels C and D, each experiment was repeated three times.