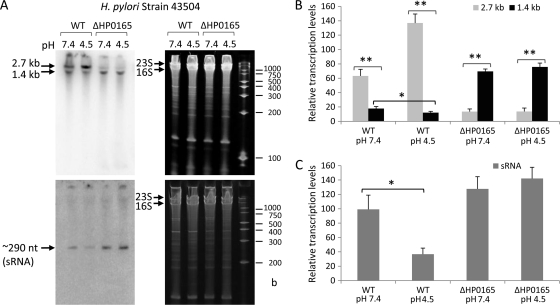
FIG. 4.
The pH-responsive expression profile of an antisense sRNA in H. pylori by Northern blot analysis. (A) The total RNAs from H. pylori 43504 wild-type (WT) and 43504/ΔHP0165::Km mutant strains were harvested after treatment at pH 7.4 and pH 4.5 for 30 min. RNA samples (5 μg) were separated in 6% polyacrylamide-urea gels and then transferred to a Zeta-Probe GT membrane. The ureAB transcripts were detected with a strand-specific oligonucleotide antisense probe (5′-ureB 2-1AS) (top panels), and the sRNA was detected with an oligonucleotide sense probe (5′-ureB 2-1S) complementary to the 5′ ureB (bottom panels). RNA samples were run alongside RNA Century Marker-Plus size markers (Ambion) with the indicated sizes. The gels (stained with ethidium bromide) are shown as loading controls (right panels). The relative transcript levels normalized to the corresponding intensity of 23S and 16S rRNA for intact 2.7-kb and truncated 1.4-kb ureAB transcripts (B) and ∼290-nt 5′ureB-sRNA (C) from H. pylori 43504 wild-type and 43504/ΔHP0165::Km mutant strains under different pH conditions are shown in the bar graphs. Error bars represent standard deviations from three hybridization experiments with independently prepared RNA samples. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005.