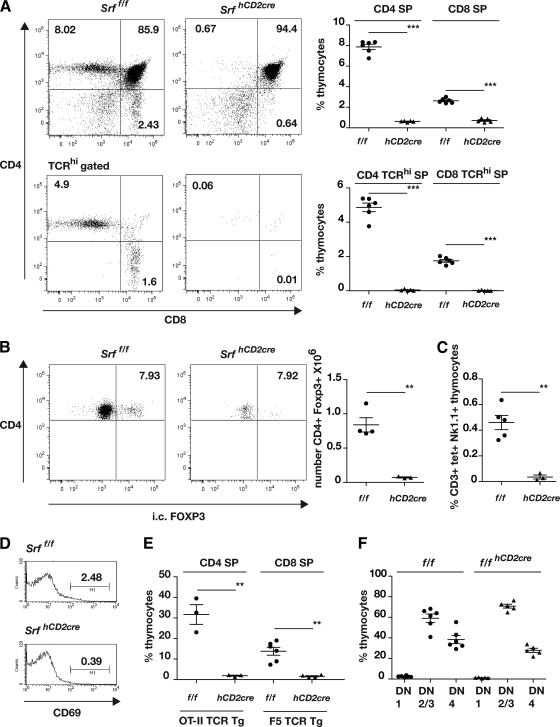
FIG. 1.
Thymocyte development in Srf mutant mice. (A) SRF is essential for thymocyte positive selection. Left, representative CD4/CD8 profiles of Srff/f and SrfhCD2cre thymocytes, without or with gating for TCRβhi cells. Right, summary of the data as scatter plots. (B) SRF is essential for the generation of thymic regulatory T cells. Left, representative CD4/FOXP3 profiles of Srff/f and SrfhCD2cre thymocytes. Right, numbers of CD4+ FOXP3+ cells, shown as scatter plots. (C) SRF is essential for NK T-cell development. Proportions of CD3+ Nk1.1+ CD1d/PBS57 tetramer (tet)+ cells are summarized as scatter plots. (D) Reduced CD69 expression in SrfhCD2cre thymocytes. Data are plotted as histograms. (E) Defective selection of OT-II and F5 TCR-αβ transgenic thymocytes in SrfhCD2cre mice. Data are summarized as scatter plots; for primary data, see Fig. S2B in the supplemental material. (F) DN thymocyte distribution is unperturbed in the absence of SRF. Data are summarized as scatter plots; for primary data, see Fig. S2C.