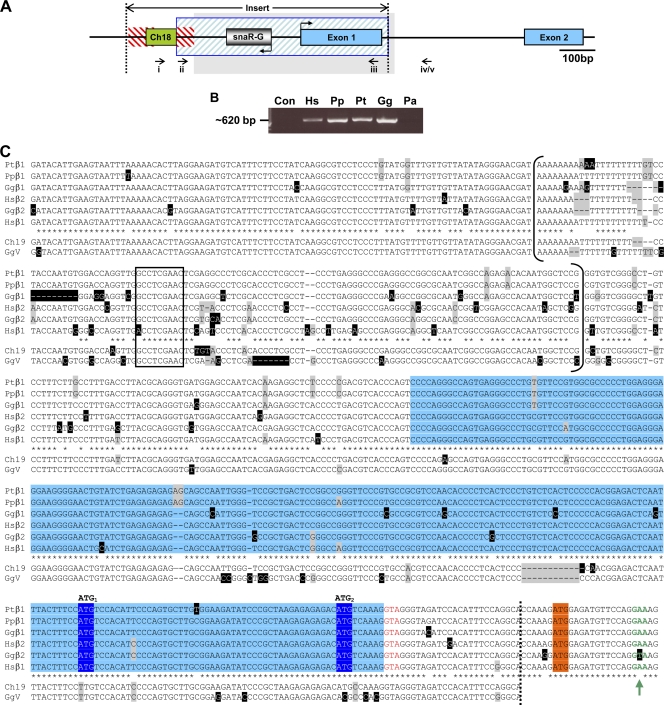
FIG. 2.
Sequence of the type II insert in African great apes. (A) Schematic of the type II CGβ insert (between dotted lines) in the context of CGβ1/2 gene structure (exons in blue). Homology to chromosome 18 (green box), Alu (red hatching), and upstream chromosome 19 sequence (blue hatching) is shown. Bent arrows denote snaR-G and CGβ1/2 transcription directions. PCR forward primers targeting genomic sequence downstream of snaR-G1 or -G2 (i) or snaR-G1 (ii) were coupled with reverse primers targeting hCGβ1/2 exon 1 (iii) and intron 1 (iv) or chimpanzee CGβ1 intron 1 (v). The region shaded gray is aligned in panel C. (B) Ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel of PCR amplification products obtained with primers i and iii, specific for hCGβ1/2 promoter and exon 1, and 293 cell (Hs), bonobo (Pp), chimpanzee (Pt), gorilla (Gg), or orangutan (Pa) genomic DNA or no template (Con). (C) Sequence alignment of African great ape genomic DNA from the CGβ1 and -β2 proximal promoter and first exon (blue shading). snaR-G genes are bracketed, and their B-box promoter is boxed. Upstream chromosome 19 (Ch19) and GgV clone sequences are also aligned, and the limit of their homology is demarcated by the dotted line. Nucleotide heterogeneity is highlighted in gray, and unique bases are highlighted in black. Asterisks denote identity among all sequences except Ch19 and GgV. Putative CGβ1/2 start codons (ATG1 and ATG2) are shaded dark blue, and the start codon of the CGβ antecedent is shaded orange. The new splice donor site (red text) and the consensus splice donor site (green text and arrow) are shown.