FIG. 2.
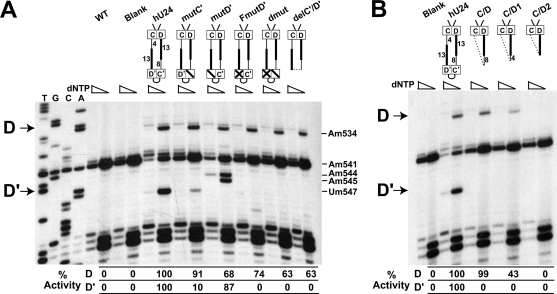
The terminal box C/D RNP can guide nucleotide methylation independent of the internal C′/D′ RNP. (A) Box C/D RNP-guided nucleotide modification is independent of the C′/D′ RNP. Schematic presentations of hU24 and its mutant constructs are shown at the top of the appropriate gel lanes, with decreasing nucleotide concentrations in the primer extension assay indicated. Primer extension sequencing lanes are at the left, and the indicated primer extension control assays include cells transformed with no plasmid (WT) and empty plasmid (Blank). C′ and D′ mutations included alteration of the K-loop GA residues alone (indicated by a slash in the respective box) and in conjunction with loop mutations (indicated by an X in the respective box). The deleted C′/D′ motif is indicated by a dashed line. Termination sites due to box C/D RNP- and C′/D′ RNP-guided nucleotide modification are indicated on the left as D and D′, respectively. Altered methylation levels with respect to wild-type U24 are indicated below the respective gel lanes. A strong termination site seen between the hU24-targeted nucleotides is the naturally methylated A541 nucleotide. (B) The box C/D RNP requires a minimal size for box C/D RNP-guided nucleotide modification activity. Schematic presentations of full-length and shortened hU24 snoRNAs are shown at the top with targeted nucleotide methylation indicated on the left by D (A534) and D′ (U547). Altered methylation levels with respect to wild-type U24 are indicated below the respective gel lanes.