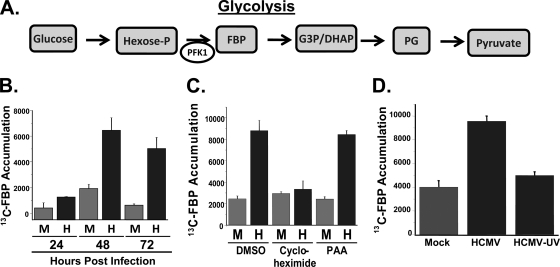
FIG. 1.
Impact of HCMV infection on glycolysis. (A) Representation of the major intermediates of the glycolytic pathway. Through a series of enzymatic reactions, glucose is converted into the final product of glycolysis, pyruvate. Both the conversion of glucose to hexose phosphate and the conversion of hexose phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) are ATP-dependent and are rate-limiting steps of glycolysis. Hexose-P, glucose-6 phosphate and its isomers; G3P/DHAP, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate; PG, phosphorylated glycerate isoforms. (B) Time course of glycolytic flux activation. Serum-starved MRC-5 human fibroblast cells were mock infected (M) or infected with HCMV (H) (MOI = 3). Cells were labeled with [13C]glucose containing medium at 24, 48, and 72 h postinfection for 1 min. After the labeling, metabolism was quenched by the addition of cold 80% methanol. Accumulation of [13C]fructose-1,6-bisphosphate was measured upon [13C]glucose pulse via measurement by LC-MS-MS. Values are means ± standard errors (SE) (n = 4). (C) Serum-starved MRC-5 fibroblasts were mock infected or infected with HCMV (MOI = 3). After adsorption, cells were treated with DMSO, an inhibitor of protein synthesis, cycloheximide (10 μg/ml), or an inhibitor of viral DNA replication, PAA (50 μg/ml). At 48 hpi, cells were labeled with [13C]glucose containing DMEM for 1 min, quenched with cold methanol, and processed for LC-MS-MS analysis. Values are means ± SE (n = 4). (D) Serum-starved MRC-5 fibroblasts were mock infected, HCMV infected, or infected with UV-irradiated HCMV (MOI = 3.0). At 48 hpi, cells were labeled with [13C]glucose containing DMEM for 1 min, quenched with cold methanol, and processed for LC-MS-MS analysis. Values are means ± SE (n = 2).