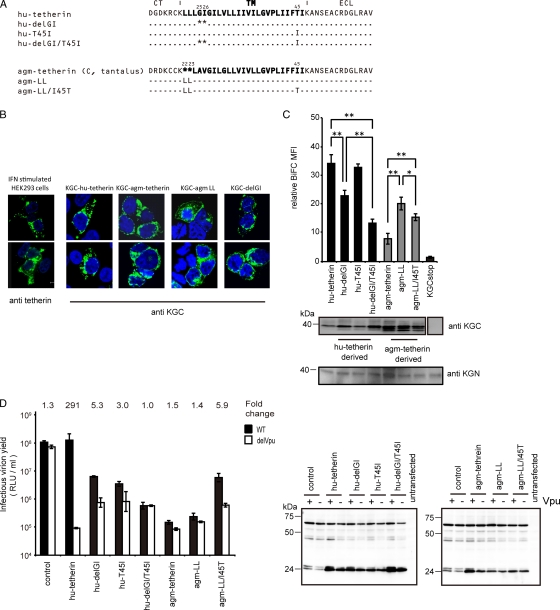
FIG. 4.
C-terminal motif in tetherin TM domain is a determinant for Vpu counteraction. (A) Amino acid alignment of hu-tetherin, agm-tetherin, and their mutants. Identity is indicated by dashes, and sequence gaps are indicated by an asterisk. (B) Subcellular localization of tetherin 2-amino acid-deletion mutant or insertion mutant. KGN-Vpu-expressing cells were transfected with plasmid encoding KGC-tagged hu-tetherin, KGC-tagged agm-tetherin, or their mutants, respectively, and cells were stained with an anti-KGC antibody. IFN-treated HEK 293 cells were stained with an anti-tetherin antibody. Cells were examined by confocal microscopy. (C) BiFC assay of hu- and agm-tetherin TM mutants on Vpu interaction. KGN-Vpu-expressing cells were transfected with plasmid encoding KGC-hu-tetherin, KGC-agm-tetherin, or the mutants and was analyzed by flow cytometry. The expression of the protein in cell lysates was detected using the indicated antibody. Relative MFI values are defined as the MFI of pKGC-tetherin or its mutant transfected cells minus the MFI of untransfected cells, and results represent the means from three independent experiments plus standard deviations. (D) Tetherin activity and Vpu sensitivity assays of hu- and agm-tetherin TM mutants. HEK 293 cells were cotransfected as described in the legend to Fig. 2B without (control) or with 100 ng KGC-hu-tetherin or agm-tetherin and the derivative DNA. The HIV-1 proteins (Pr55Gag) in the cell lysates were detected using anti-p24 antibody. Results represent the means from three independent experiments plus standard deviations.